How to transplant grapes to another place?

Growing grapes has always been considered difficult and expensive, but thanks to modern knowledge and technology, it can be grown even at home. The need for grape transplantation occurs quite suddenly and is a difficult process, but quite feasible. This practice was carried out for centuries and during this period it became well-established. As in any such tasks, the main thing is to follow the basic rules and the result will meet all your expectations.
Features depending on age
Let's start with the young shoots of grapes. One of the most common methods of reproduction of grapes - cuttings. They are placed in the same bed, called shkolka, and leave them until they reach the age of one year. At this age, the grape has the appearance of a small bush with several shoots and has such a property as the highest rate of survival.
Relatively easy to transfer to a new place and a two-year sapling. As a rule, at this age, the plant already has a formed root system, though not as strong as that of the old grapes, but already a solid above-ground part. After transplantation, it is best to leave a pair of eyes, from which new shoots can then be formed. Such a small amount of shoots is needed for easier formation of the subsequent shape and direction of grape growth.
An adult shrub, unlike a young grape, tolerates transplant quite hard. Its formed and strongly overgrown root system will require a long period for adaptation. Such is the three-year grapes. In this case, the minimum distance that the plant should be dug in order to avoid damage to the root system is half a meter. A three-year-old seedling needs to leave about 5 eyes so that in a new place it can better absorb moisture and useful substances from the soil.
Transplantation of four-year grapes should be done with great care. In this case, there is a need to dig a large hole for a massive root system. The same applies to grapes aged about 5 years.
It is not recommended to replant bushes older than 5 years. At this age, the plant has a high probability that the grapes will not take root, and the main reason for this is that the overgrown root system cannot avoid damage during digging and transfer to a new place. Above all, you need to know that the bushes younger than this age begin to bear fruit only after several years of adaptation in a new place.
Despite these recommendations, there are known cases of successful grape transplantation at the age of 7 years and 10 years.
One of the most important features that applies to any old grape is that they are sensitive to the magnetic fields of the Earth. It is best to plant the old bush in a new place in the same location in relation to the cardinal points, which was in his place.
Timing
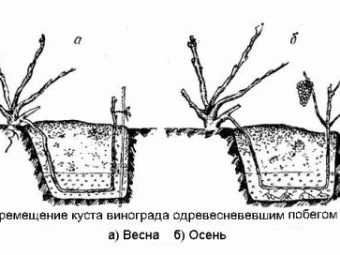
Spring transplantation is the most favorable, since in the subsequent warm time the chances of taking root in the new soil of the grapes increase significantly, and by winter the plant will already be finally ready for the cold period.
It is necessary to carry out a transplant within two weeks in the interval from the swelling of the cuttings to the blooming of the kidneys, as well as the appearance of the first leaves. The starting point of the process can be considered the beginning of sap flow. When several bushes are transplanted, some of them are transplanted in the autumn in order to clearly determine the survival rate of the first batch.
Autumn transplanting is permissible for hot southern regions. Too much heat, like cold, can have a detrimental effect on newly transplanted grapes. With a high probability of a hot summer, which is fraught with frequent droughts, a transplant in the autumn will help the plant to get used to the new place more easily.
It is best to start a transplant after the first buds appear on the vine.
As an alternative, another more visual way is used to check whether the grapes “woke up” after winter - it’s enough to cut the stem of the plant 1 or 2 cm deep; if the juice goes, it means the plant has successfully overwinter and you can start transplanting. On average, such a period of grapes comes in the spring in April, less often - in May. Ideally, transplanting should be done as soon as the soil temperature reaches +8 degrees. It is important to bear in mind that The temperature of the air and the temperature of the soil in spring vary greatly, and in this case it is necessary to measure only the temperature of the soil to which grapes are to be transplanted.
In the summer of transplanting is not recommended, the likelihood that the vine will take root in the hot season during its flowering or fruiting, is significantly reduced. At this time of the year, grapes can be transplanted only out of urgent need, and after that it is necessary to cover it from the sun for a while.
The autumn grape transplantation is also practiced. It is best to carry it out after complete abscission of the leaves, but before the first strong frosts. The roots will be able to take root only in the warm ground due to the fact that the upper part of the plant has already ceased its activity. This practice occurs only in regions with a warm autumn. The best time for an autumn transplant in warm regions is mid-November.
In Moscow and the Moscow region, grapes are best transplanted in late April - early May.
Where to plant?
The need for transplantation is most often associated with the fact that grapes grow poorly in the old place. Grapes grow poorly in windy places, which can also cause transplantation. Sometimes a new, more sunny place in the same area has a beneficial effect not only on the plant itself, but also on the future harvest.
It is well known that grapes love heat and light, which most often distinguish the southern and southwestern slopes.
In addition to the need for a large amount of light, grapes need a vertical surface around which it could grow. As such a support, the same southern or south-western slopes and fences are best suited.
When transplanting grapes, it is recommended to locate along the magnetic line of the Earth, from north to south. Except when the grapes are older than 5 years. As mentioned above, the old grapes should be located in relation to the cardinal points in the same way as it was located in the old place.
Considering the composition of the soil in a new place for grape transplantation, it should be remembered that this culture is not exactly familiar in the marshes and salt marshes.
The neighborhood with other plants is destructive for grapes, and both with other grapes, and, for example, with a tree. In the first case, the shoots will interfere with each other due to the fact that they will be intertwined, and in the second, the grapes will braid the tree and climb to the very top, where it will be difficult to harvest.
Unfortunately, there are situations when the grapes are planted in an old pit from a uprooted stump or another plant. This is strictly forbidden, since the soil in this place is no longer a nutrient medium, the soil simply begins to suffer from "fatigue." The second weighty reason for not doing this is the presence of inhibitors of another plant. These substances inhibit the root system of other seedlings. A sapling at best will grow poorly and often hurt in such an environment, or it may simply die.
Training
Immediately it is worth noting that the preparation of high-value varieties and ordinary varieties occurs in different ways. Ordinary varieties do not require special preparatory processes, while for valuable varieties the opposite is true. Ordinary varieties can simply be dug up and planted in a new place, after completing the process of watering them with water. For valuable varieties, things are a little different. We will talk about this below.
The preparatory stage begins a year or even two before the intended transplant.Approximately from this time they stop removing the dew roots, which we will discuss in more detail in the chapter below. As a rule, this is done in order to make the grapes better settled in a new place with the help of their superficial and deep roots.
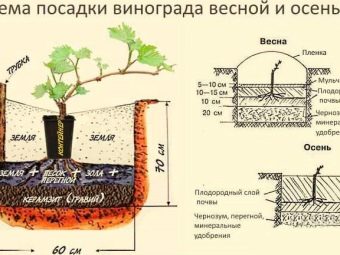
The next step is a preliminary digging, the purpose of which is to adapt the plant to a new place. This stage is made after harvesting and at the same time the grape trunk is dug round in a narrow groove, the size of which should not exceed half a meter. These are medium sizes; for an old plant, a groove will be deeper - about 60-80 cm.
Then it is necessary to fill the fresh trench with fertile and loose soil, and then abundantly shed it to the full depth. As a rule, after a properly performed process, many young roots will appear around the trunk.
In addition, it must be borne in mind that the more transplanting takes place in a colder time, the more intensively the roots must be pruned. As a rule, it is recommended to leave a pair of ocelli on the sleeve and the same on the shoots.
As for the size of the landing pit, it should be spacious for the rhizome. You should also know that the dimensions of the pit may also depend on the place where the grapes grow: in the southern regions it must be deeper, since the roots will grow down more intensively than in other directions because of their desire for groundwater, and in the northern regions The plant system is located on the surface layers of the soil, tending to heat, which implies a wider pit.
It is important to know that after such changes the grape harvest will be reduced at least twice.
At home, the simplest method of transplantation is used - using cuttings. One of the obvious advantages of this method is simplicity. Cuttings are easy to plant and grow at home. Pots for them are often plastic cups. Cuttings are considered ready for transplanting only when the first leaves appear on them. During the whole process, two factors are important.
- The correct time to start planting cuttings is the end of February or the beginning of March.
- You must choose those grapes that are easily mastered in a new place. The category of such varieties includes "Delight", "Annie", "Veles", "Laura" and others.
Preparation for transplantation can take place in different ways and almost always with a positive result, but it is important only in both ways to adhere to the correct dates for all stages.
How to transplant?
It is impossible to say in advance how correctly this or that stage will be passed during grape transplantation; a good result is not always guaranteed. Below is a simple step-by-step instruction.
- To transplant grapes to another place, choose a cool, cloudy day or twilight time. A few hours before the transplantation process begins, the grapes are watered abundantly with water, and it is important to choose the right temperature - it should be warm.
- The next step is digging a hole for seedlings. After a well-sized pit has been dug, it should be filled with two or three buckets of water. It is important to form a small slide at the bottom of the pit so that the air does not linger there later. Sometimes a pit dug for grapes is poured with hot water; after transplantation, the upper part of the plant is buried with earth. Taken together, this helps the roots to settle faster and slows the growth of the aerial portion of grapes. But this is only a recommendation, and such a process should be carried out with great care in order to avoid unpredictable results.
- The main stage is the transplanting of a plant to a new place. This step can be divided into several stages - first you need to dig a plant. As mentioned earlier, you need to dig a groove around the plant. Most often, this is done using an iron sheet, which is placed around the perimeter of the coma and fastened with wire. After the "boundary" is scheduled, begin digging.After the root system becomes visible, large or intolerable roots are cut. With the help of two shovels, the plant is pulled out of the pit, placed on a tarp or stand.
In addition to all of the above, there are some specific transplant methods:
- transplanting with a big lump of earth;
- transfer with a small (shortened) clod of earth;
- transplanting as a seedling.
A transplant with a big lump of earth is the best option for transplanting. With this method is the least damage to the root system.
Important in this process is the knowledge of the types of roots: root shtamb, heel roots, median roots and dew roots. The main absorption of nutrients occurs at a depth of 30 to 60 cm and is performed by heel roots. But the absorption also happens with other roots. You need to know this in order not to accidentally damage the heel roots. If the damage to the roots still happened, then the roots with a diameter of a couple of centimeters can be easily restored within a few months, but the likelihood of the restoration of roots thicker than 4 cm in diameter is practically excluded.
The older the grapes, the more he should have when transplanting.
Can I do without a transplant?
As mentioned earlier, seedlings over 5 years old are not recommended for replanting. Unfortunately, this is the case when it’s not that you cannot do without a transplant, but rather you cannot do it at all.
The need for grape transplantation occurs only when redevelopment of the site is required or when the plant lacks sunlight. In all other cases, it is better to refuse to transplant grapes. The very process of growing grapes is time consuming, as this crop is a rather capricious plant that requires regular maintenance. Therefore, the additional complication of the process of growing grapes by transplanting can lead to a not entirely successful result.
A good alternative to transplanting ordinary grapes is the so-called wild grape. It is unpretentious and can grow quite rapidly in a short time, and sometimes even behaves aggressively.
It does not require special care, but, unfortunately, is not very fertile and sits as a decorative “living” wall. Most often, he landed near the gazebos, walls or other vertical surfaces. This grape requires care only in the sense that it will be necessary to regularly prune some shoots, as they are capable of destroying brick and stone walls.
Grape transplantation is not a very complicated, but multi-step process. A good result is more likely to be likely than a negative one. We hope that this article will help you to transplant grapes and enjoy its fruits in a short time.
For details on how to transplant grapes, see the next video.