Semi hard cheeses: Difference from hard cheeses, variety and brand

Cheese is one of the most popular dairy products in the domestic market. It’s almost impossible to imagine a daily menu without this product - we make sandwiches from it, use salads as an ingredient, prepare hot dishes, and also use it with coffee or wine.
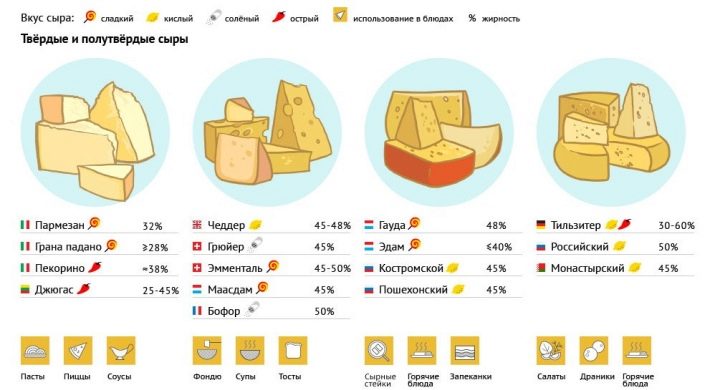
Many of us know that there are several types of cheeses. One of the classifications suggests that this product can be divided into hard, soft and semi-hard varieties. If the first two varieties are more or less clear, then semi-solid consumers raise a number of questions.
What are semi-hard cheeses?
Semi-hard cheeses have a dense structure and are not processed by a hard press. Such varieties are often covered with a thick crust or wax (sometimes such a surface film is a moldy layer).
The semi-solid product differs from hard and soft varieties in its structure. In addition, it is subjected to pressing in other ways and has a different ripening period.
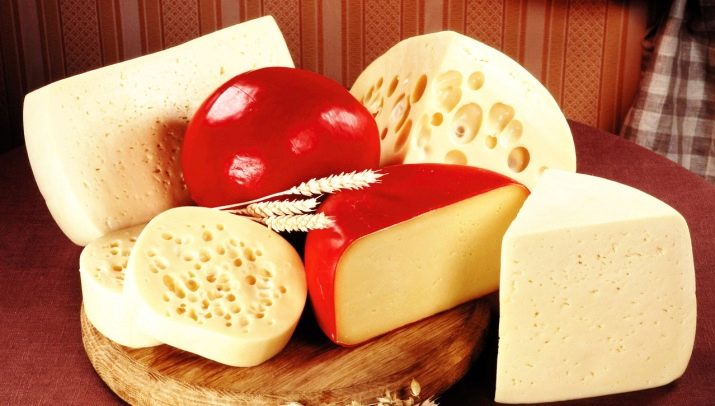
Such a product is sold in almost every supermarket, store and in every market, it is available to any buyer. A distinctive feature of some varieties are the notorious holes in the cheese, they can be round or oval.
What is the difference between species?
Solid and semi-solid product varieties differ in a number of ways. Among them are the consistency and structure, ripening and much more. Consider more such differences.
- Structure. Solid varieties have a crystalline structure, they are tough, dry and crumbly. Semi-hard is much softer in its consistency.
- Maturation term. The term of ripening of semi-solid varieties is calculated in months, while the solid - in years.
- Taste and aroma. The solid ones have a brighter taste and are more fragrant, semisolid ones are more neutral and soft in taste.
- Shelf life. Hard cheeses are stored longer semi-hard.
- Use in cooking. Semi-solid varieties are more often used for cooking hot dishes (for example, cheese omelet or pizza), while solid ones are an exquisite product, they are more often eaten as an independent snack.
Production secrets
A product of this type is manufactured within 1–1.5 months. Such a short production time plays into the hands of the consumer and contributes to the formation of affordable and affordable prices. The recipe for making semi-hard cheese is quite simple. The initial product is obviously milk (cow, goat sheep or any other is used).
First, the milk is subjected to heat treatment, due to which it is brought to a state of cottage cheese. The flow of such processes is provided by means of special enzymes and starters (rennet elements can also be used). Then the whey is separated from the finished curd - for this, the curd is pressed, steeped in brine. After that, the semi-finished product must ripen (it is this process that takes 1–1.5 months).
Already the finished product is on the shelves of supermarkets, where it falls into the consumers' refrigerators. Remember that the shelf life is about 1 month, so be sure to read the packaging. All semi-hard grades are made. according to GOST standards with the observance of production technology and technical conditions.
Nutrition and energy value
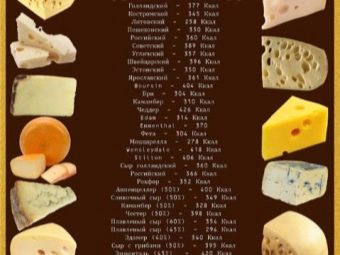
Among cheeses, soft varieties have the least calories. Solid and semi-solid varieties contain significantly more kilocalories. The difference is significant - for example, 100 grams of Russian cheese contains about 400 calories. For comparison, there are 350 calories per 100 grams of Dutch and Maasdam. As you can see, this product is not suitable for those who want to lose weight, keeps himself in shape and looks after the figure.
According to nutritionists, in semi-solid cheeses, 100 grams of a product contains 24-27 grams of protein, 14-28 grams of fat, and up to 2 grams of carbohydrates.The described indicators can vary significantly from the type of cheese and the milk from which it was produced.
Varieties and brands
Among semi-hard cheeses, both domestic brands and yellow cheeses imported from abroad are very popular. Consider recognizable names in more detail:
- Russian young - a product of domestic production. It is produced in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus and Latvia, prepared from cow's milk;
- Kostroma - one of the most common species that has been known and popular since the days of the Soviet Union;
- Uglich - for the first time in history it was produced in the first half of the 20th century (1935), a universal brand;
- Yaroslavsky - has a spicy taste;
- Imperial - made from the highest quality milk;
- Estonian - has an elastic structure and sour notes in taste;
- Latvian - one of the fattest grades;
- Cantal (Cantal) - one of the oldest varieties, whose birthplace is France;
- Edam - a product of Dutch production, produced in the form of round heads and has a nutty taste;
- Gouda (Gouda) - a product with a fat content of about 50%, prepared from cow's milk in Holland.
- Roquefort - Delicious semi-hard cheese with mold.
Use in cooking
Cheese is a popular ingredient in many high and home cooking dishes. Pizza, croutons, pasta and many other dishes are made from it. One of the most interesting recipes is a salad, for preparation of which you will need cheese, carrots, ham or sausage, chicken eggs, potatoes, pickled cucumbers, greens and spices. Another popular dish is cheese croutons. For cooking you will need only a few ingredients: cheese, bread, butter (preferably cream) and garlic.
Cheese is a favorite milk product. It is an integral component of the daily breakfast, eating pizza in a friendly company and cooking homemade toasts. The most popular and affordable among all varieties of the product is semi-hard cheese. One of the reasons for the wide distribution of the product is the affordable price. In more detail with the classification of cheeses, you can see below.