Soft cheese: types, varieties and homemade recipes

Cheese lovers probably know that the most important difference between different sorts of cheese is its consistency. Based on this basic principle, hard and soft varieties are distinguished. Soft cheeses got their spread much later than hard, and are still considered a more delicacy and elite product.
Description and classification of soft cheeses
Soft cheeses, as a rule, are distinguished by a high fat content, since they are made on the basis of milk with the addition of rich cream. It is this natural composition that justifies their pronounced creamy taste. It is also worth mentioning the shelf life of soft cheese - it does not exceed 3-4 days.
In the production of soft varieties, no pressing is used, all products of this type are self-pressing.
The main types of soft cheeses, depending on the microorganisms used to create them, are:
- with white mold;
- with blue mold;
- fresh;
- with washed crust (slug).
Classified by type of milk used:
- based on cow's milk;
- based on sheep's milk;
- on the basis of goat milk.
Name Varieties
The most common white-mildew varieties owe their appearance to France.
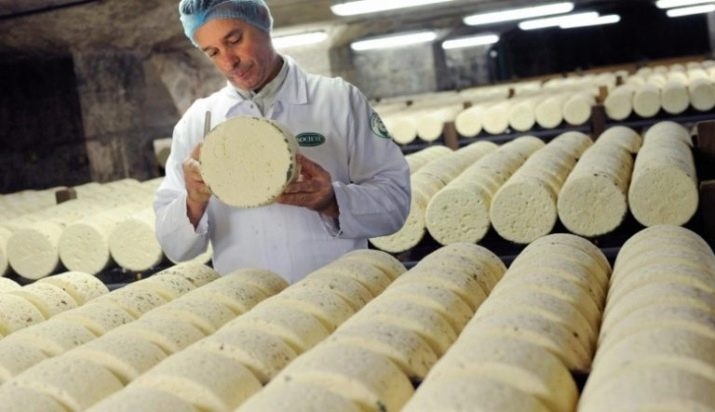
- Brie - classic soft variety with a dense moldy crust, the progenitor of all cheeses with white mold. It is made in the form of a circle of different diameters from 30 to 60 centimeters and a height of 3 to 5 cm.
- Boulet d'Aven - the most stuffy and soft, formed in the form of a cone with a white-red or white crust.
- Camembert - similar to Brie, but produced under other conditions, which provides him with a more pronounced creamy taste and mushroom aroma. Also, its distinguishing feature is the packaging made of wood. It is produced in a strictly fixed size - 11 cm in diameter.
- Cambozola - combines white and blue mold.
- Caret - Brie differs from lower fat content.
- Neuchatel - distinguished by its original shape in the form of a heart.
- Rougette - soft, covered with white and red mold.
Blue mold cheeses are produced using the strain of penecillium roqueforti, which gives these varieties a special spicy flavor and strong aroma.
The most common varieties are listed below.
- Roquefort - the only one from the blue mold family of cheeses is produced on the basis of sheep milk. It is made in certain caves in a small area of France, and therefore has a high cost.
- Dorblu - German variety, has the mildest taste of all blue cheeses, for which he received his recognition in our country.
- Gorgonzola - Italian common variety with blue mold, characterized by increased sweetness. It has a sharp bright taste.
- Bleu de bresse - the youngest of this family, ripens quickly, has a very soft taste without typical spiciness.
- Lance d'Ambert - the most tender variety of “blue”, round shape, covered with gray or red mold crust.
Fresh cheeses are produced either with the addition of rennet and yeast, or based on fermented milk sourdough only, without the fermented component.
The latter is often called fermented milk. All varieties of this type have a very short shelf life, almost no ripening time.
- Ricotta - Whey variety originally from Italy. It is a by-product after making other types of cheeses.
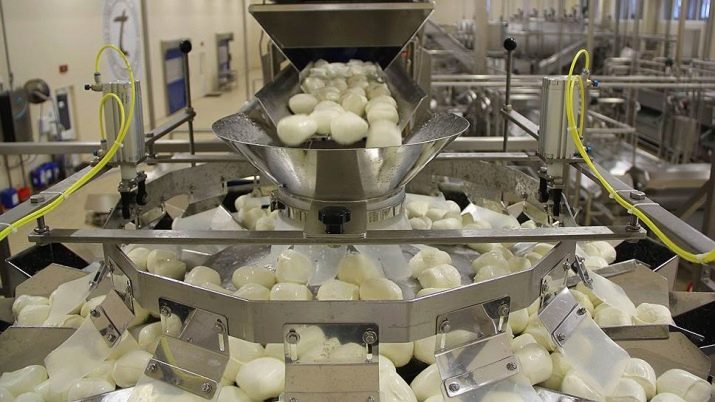
- Mozzarella - young brine type cheese which is formed in the form of balls and placed in a brine.
- Burrata - made in the form of a bag filled with mozzarella pieces and cream.
- Adygei - common in Russia, a variety produced without ripening, has a white color and a pure, sour-milk taste. As a rule, it is unsalted, with additions of dill and garlic.
- White cheese - fermented milk pickle cheese produced from any kind of milk.
- Feta - Greek pickled cheese from sheep and goats milk.
Cheese with rinsed crust is another kind of soft cheeses, to which special slug bacteria are added. The ripening surface of this type of cheese is regularly washed with a strong salt solution made according to special recipes in each country. Wine, beer and other components are often added to the brine, which make the taste of this product special and rich. Here are the main varieties with washed rind.
- Langre - a classic short-ripened variety with washed crust, produced on the basis of cow's milk. Has a salty soft taste.
- Livaro - Norman cheese, longer exposure than Langres, with a yellow-brown crust. It has a pronounced savory taste; the longer his exposure, the greater his sharpness.
- Mont d'Or - the variety with the softest consistency of this type, it is used with a spoon. White crust makes it similar with white mold cheeses. Soft creamy taste with mushroom flavor.
- Münster - the most popular French variety with a golden crust. Washed with brine with the addition of cumin and cumin, which gives it a special spicy smell, while maintaining a creamy taste. It has a fairly dense structure.
- Epuass - has a bright aroma of grape vodka, combined with a delicate sweet-salty taste. The owner of a bright red crust.
- Pont l'Eveque - has an unobtrusive savory taste, salty, with a sweet aftertaste. Enough dense texture.
Benefit
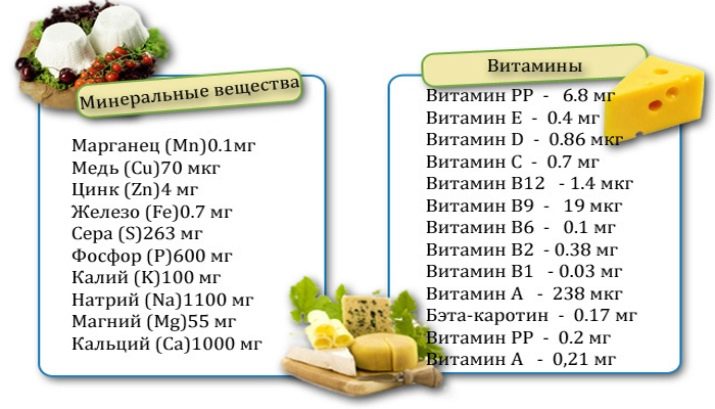
In addition to the taste variety, cheeses contain a large amount of beneficial vitamins and trace elements, positively affecting the functioning of the body:
- high content of vitamin C serves to support immunity;
- B vitamins regulate the nervous system and are responsible for resistance to stress;
- a large amount of protein, calcium and phosphorus has a positive effect on the musculoskeletal system, strengthening the bones and reducing the risk of developing unpleasant diseases, such as osteoporosis;
- Among soft cheeses, many contain low amounts of fat (for example, Adyghe, mozzarella, ricotta), which makes them a valuable dietary product in the fight against excess weight;
- the content of such minerals as potassium and magnesium has a positive effect on the work of the heart and blood vessels;
- the presence of beneficial fatty acids makes cheese a safe product for people with high cholesterol;
- The Adyghe champion is the record holder in the amount of vitamins in cheese: in its composition vitamin E, vitamin A, and vitamin D3 are contained in a digestible form;
- the maintenance of irreplaceable amino acids is extremely important for support of activity of an organism;
- in the presence of allergic reactions, it is recommended to use goat cheese, which is completely hypoallergenic. Also, goat's milk is easier to digest, contains more vitamins with a lower fat content of the product;
- moldy cheeses have an increased ability to absorb calcium from them;
- noble mold covering cheeses has a positive effect on digestion, prevents bloating and diarrhea, provides a favorable intestinal flora.
Possible harm
Eating any food must be controlled, This is especially true for moldy cheeses:
- the use of moldy cheeses should be limited to 50 grams per day, since the penicillin fungi in their composition can suppress the natural intestinal microflora and cause damage to it;
- mold can cause an allergic reaction;
- in case of fungal diseases in the body, the use of these products may aggravate the course of the disease;
- It is necessary to abandon the use of moldy cheeses during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as they can not eat young children.
As for the soft cheeses without mold, they also have a number of recommendations:
- it is necessary to refuse their use to people with high cholesterol and atherosclerosis;
- in diseases of the liver and pancreas, it is worthwhile to limit the consumption of cheese on the basis of sheep milk;
- soft cheeses have a fairly high calorie, so you should give up their use to people with excess body weight;
- salt content in brine varieties is large enough, so people with hypertension should refuse from their presence in the diet;
- for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract should be excluded from the menu fatty cheese varieties.
Production technology
The main distinctive features of the production of soft cheese varieties are:
- long pasteurization and high-temperature pasteurization;
- use in all cheeses of lactic acid bacteria;
- ripening time depends on the variety, ranging from 1 to 45 days;
- in the production of cheese mass is not heated a second time;
- the use of increased doses of starters, due to which a more dense and durable clot is formed;
- high moisture content at the time of ripening and in the resulting product.
If you break the production technology of soft cheese into stages, they will be as follows:
- milk preparation;
- adding clotting agents;
- work with a clot;
- molding and pressing;
- salting;
- maturation.
Milk preparation is one of the most important stages, the result of which will greatly influence the resulting taste of the product. First of all, the milk is mechanically cleaned of impurities, after which it is subjected to heat treatment in order to destroy pathogenic bacteria and suppress the vital activity of microorganisms in it. Depending on the production conditions, several types of heat treatment can be used. Next, the milk is homogenized.
During the pasteurization process, the ability of milk to coagulate is significantly reduced, therefore calcium chloride CaCl2 is added to it, which stabilizes the resulting cheese clot.
Also, to standardize the production of cheese, milk before cheese making is normalized to a certain parameter of fat content.
The next step is added to the milk bacterial starter, which contains aromatic components. Using sourdough without aromatherapy streptococci, it turns out sour cheesy crumbly cheese. Also, depending on the type of cheese, moldy cultures or bacteria of cheese mucus are added.
Next, rennet added to the milk heated to 35 degrees with added yeast is added, which is responsible for the formation of a cheese bunch consisting of milk protein, casein. After the formation of a stable clot, it is cut to accelerate the process of extracting serum. Then, depending on the variety, the mixture is either reheated or stirred without heating.
When the cheese grains become sufficiently dense, the kneading of the mass is stopped, and they proceed to the process of molding the cheese. To do this, use a special basket for decanting serum. Depending on the type of cheese, it should stay there from 20 minutes to several hours. This is followed by a salting step; salt solution is most often used, but rubbing of the heads with fine salt and salt floor can also be used.
Next, the cheese is sent for ripening. During this process, the heads need to be turned regularly. Varieties that do not require ripening can be immediately consumed.
Simple recipes
At home, you can make cheese using simple ingredients at hand, it is not a very time consuming process.
Recipe with kefir
Pour the milk into a deep pan and put it on the stove, bringing it almost to a boil. Pour in kefir and stir constantly. When the curd grain is separated from the whey, you need to turn off the heat and salt the mass. Such cheese can be thrown back into a special basket for the formation of cheese or in a colander, covered with densely folded gauze. After the whey is drained, you can add herbs or spices to the cheese, then mix and put it under a press.
Recipe for frozen kefir
Freeze 1 liter of kefir; it is important that it be completely frozen.Cover a colander with gauze and put frozen kefir in it, after which it should be sent to the refrigerator until it is completely defrosted. When all the serum is drained, a gentle cheese cream will remain in the gauze.
How to make soft cheese at home, see the next video.