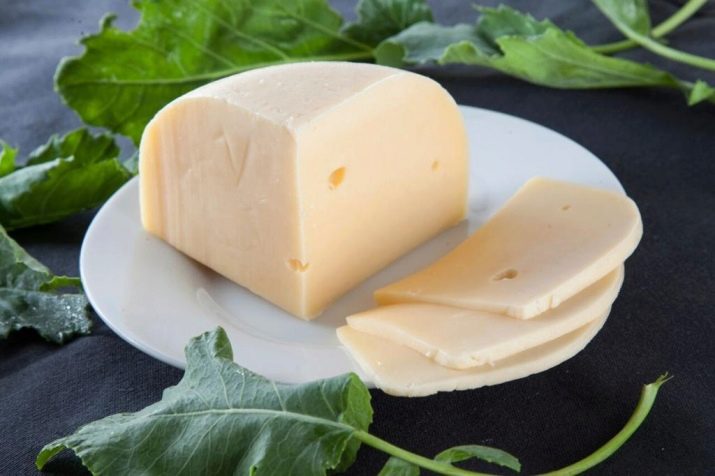
Sourdough cheese: what are, how to choose and how to cook them at home?

Beginning cheese makers can be difficult to determine the types of sourdough cheese. What types are there, how to choose them and cook with their own hands at home?
These questions will be answered by our article.
Kinds
In order to form a protein clot - cheese base from liquid milk (cow, sheep, goat), ferment and enzymes must be added to it: mandatory ingredients in cheese production.
Sourdough differs from enzymes in its function - it contains bacteria of various cultures that eat the milky environment and secrete the processed acid. At the same time, enzymes make milk faster and more efficiently.
According to the types of sourdough, they differ and directly determine the texture, ripening time, aroma and taste of each type of cheese. There are the following types of starters.
- Mesophilic or cold starters, they work (grow and multiply) at a low temperature (27-30 ° C). On their basis they make cheeses with a low cooking temperature - up to 38-40 ° C. Vivid examples of such products are Cheddar, Russian, Dutch, a number of brine, rennet, soft and hard, without peepholes cheeses, in the production of which are used bacterial cultures of Leuconostoc lactics (subspecies lactics and cremoris).
More than 50% of all cheeses are made using mesophilic starters. For cheese with a higher cooking temperature, another type of starter is used.
- Thermophilic starters. The condition for optimal growth is a temperature of 41-43 ° C, the highest temperature at which thermophiles do not die is 65 ° C. The relative resistance to elevated temperature of thermophiles allows you to create exhaust cheeses and varieties of reheat products, the use of which is traditional for Italy and partially for Switzerland. Among these varieties can be noted cheese Romano, Gruyere, Provolone, Maasdam, Mozzarella,
The composition of thermophilic starters include streptococcal thermophiles - a number of lactobacilli, such as:
- L'Delbrueckii, a subspecies of the Bulgarian wand;
- Lactobacillus helveticus and L'Delbrueckii, a subspecies of lactics.
But in a certain sort of cheese, bacterial cultures can also be found in mixed versions. So, recently, thermophilic starters have been used as additional bacteria in the souring of Gouda, Cheddar cheese varieties to increase acidity and improve taste.
And mesophilic ones are often used in Mozzarella for quick eating of sugars, which give brown hue to unnecessary cheese when it is heated.
For the rest of the bacterial starter cultures, which are used in milk intended for cheese, but non-starter cultures, since they do not emit lactic acid in sufficient quantities, include:
- propionic acid bacteria;
- bifidobacteria;
- Penicililum bacteria.
In the industrial production of cheeses, souring is used to maintain their constant technological quality, the basis of which contains multi-strain mixed cultures or single paired strains.
The content of lactic acid bacteria in them can be of different kinds and composition. They are continuously used in the production of traditional varieties of cheese, updated every day, using the developed leaven from the previous day.
Criteria for choosing a cheese base
When choosing the type of lactic acid bacteria for fermenting the cheese base, one should make a start from what kind of cheese should be prepared. After that, you should choose the dry starter or maternal.
- Sourdough dry It is very convenient to use and store, it is also called the ferment of direct application. It can contain both thermophilic and mesophilic cultures in dried powder form. Drying occurs under production conditions at a negative temperature of -45 ° C.Sourdough is sold through specialty stores where the dry substrate is properly stored in freezers. The ease of use of the starter starter has provided them with popularity and widespread use in small private cheese factories and large enterprises.
The use of a dry concentrate of lactic acid cultures consists in the simple addition of a powder from lactobacilli directly into milk. Powder should be poured, as if spitting milk, then gently stir, reaching the bottom of the container, give it time to soak up and activate for about 30-40 minutes (depending on the attached instructions).
- Maternal (reclaiming) leaven it is more profitable to use, but first it needs to be grown in a dairy medium from a culture of lactic acid bacteria of a certain type. The benefit is the reusable use of the updated base for cheese: it is enough to add 1-1.5% of the ferment each time from the total amount of milk. Thus, for 10 liters of raw milk, 0.1-0.15 liters of fermented product will be required. However, there are certain difficulties in the preparation of such a starter: it may become unsuitable if the sterile conditions are not fully met. When storing the parent starter, it is also necessary to observe sterility, it is stored in the refrigerator for up to three days, or up to 90 days in the freezer.
It should be remembered that updating the fermented maternal base is a reusable but not endless process, otherwise it will negatively affect the taste of the prepared cheese.
How to make a leaven at home?
You can try making homemade cheese sourdough in your home kitchen. We offer recipes for three types of recultivated (maternal) starters: thermophilic, mesophilic, and mixed.
Sourdough maternal mesophilic
First of all, you need to prepare the dishes: wash, thoroughly wash the detergent, and sterilize one-liter jar with a plastic lid. Milk for making sourdough should not be ultrapasteurized. For 1 liter of skimmed (0% -0.3%) milk, take a quarter of a teaspoon of dry concentrate of mesophilic yeast.
Pour the milk into a one-liter jar and cover with a lid, place it in a suitable saucepan, pour enough water into it so that it completely (before the coat hanger) covers the jar. Put the pot on a slow fire, wait for the boil and simmer for a little fire for half an hour. Then carefully remove the jar, leave to cool to 24 ° C.
Carefully sprinkle mesophilic leaven over the whole milk surface, wait three minutes, during which the powder granules imbue moisture. Stir thoroughly with a clean spoon, trying to distribute the granules throughout the milk volume. Put the future leaven for growth and activation of bacteria for 18 hours at a constant temperature of 24 ° C.
The resulting substance will resemble yogurt, to taste - with milky sour and slightly sweet. You can put a starter in storage in the refrigerator for up to three days or in the freezer for up to three months. Before freezing, the re-cultured leaven should be distributed in sterilized ice trays, covered with a sterile cap. Defrost mesophilic culture is better gradually, on the top shelf of the refrigerator, in any case not in the microwave.
Do not forget about the purity of hands during work, it is better to take out the frozen starter in medical gloves.
Thermophilic parent ferment
For its preparation use the same volume of ingredients: for 1 liter of ordinary non-UHT milk with low fat content (0% -0.3%) take a quarter of a teaspoon of thermophilic culture powder. A glass jar with a lid should be sterilized. You need to take good care of your hands or do everything in sterile gloves.
Put the closed jar of milk in a high saucepan filled with water, which will reach the level of milk in the tank.Slowly boil water over low heat, leave to boil for half an hour, without adding heat. Pull the jar out of the pan, cool to 43 ° C. Powder from thermophilic lactobacilli sprinkle the surface of the milk, wait 2-3 minutes. AkkuratZakvaska thermophilic maternal. o stir, reaching the bottom and sides of the jar with a clean spoon or fork.
The time of maturation and growth of bacteria will be 5-6 hours at a maintained external temperature of 43 ° C. At home, you can create it in a yogurt maker or a slow cooker. Cooked sourdough taste and similar to buttermilk, thick yogurt. At the next stage, you need a quick cooling of the finished fermented base: you need to put the jar in the refrigerator, despite the fact that it is warm.
Cooked sourdough is stored for up to three days in the fridge or frozen in the same way as mesophilic maternal culture.
Mixed mesothermophilus starter
The process of its manufacture is not much different from the previous two recipes. You need milk with low fat content and dry concentrate (powder) of mesothermophilic cultures in the same proportions.
After half an hour of boiling the jar of milk in the pan, it must be removed and cooled to 40 ° C. Then put the jar in a warm place (yogurt maker, multicooker), the temperature of which will not exceed 40 ° C. The growth and activation of lactobacilli will occur within 8-12 hours. Store the mixed mother sourdough in the same way as the previous two sourdough.
It is necessary to carefully consider the surface of the finished fermented product before sending it to storage. If after many hours of ripening of any prepared starter, bubbles form on its surface (even a single one), this means its unsuitability.
Bubbles can be created by gas - carbon dioxide, which is released by bacteria of Escherichia coli, which means that the dishes were not sterile enough. Or perhaps the milk was substandard. Although, there is an exception: for bacterial cultures of diacetylactis, small bubbles are allowed.
See how to make homemade cheese sourdough in the next video.