After what crops can you plant tomatoes?

Experienced gardeners are well aware that for a good harvest, you should not only choose the right varieties and ensure the right care, but also properly prepare the garden before each new summer season. The fact is that each plant leaves a noticeable mark on the soil in which it grew - it consumes some useful substances from it almost completely, but it can also enrich with some of them. For the same reason, tomatoes can not be planted anywhere - you must first make out which crops do not exhaust the soil so that it does not grow tomato bushes.
Planning features
You can write a whole book on how to alternate cultures correctly, but we will try to consider all the basic principles in brief. All of these principles apply to most garden crops, and therefore also concern the cultivation of tomatoes.
It is worth starting with the fact that each plant has its own pests and diseases, which are relatively little interested in other cultures. It is possible to poison insects as much as possible and to cure diseases, however, in conditions of open ground it will not be possible to achieve an absolute result - some microorganisms and pests will still hide in the soil and survive the winter.
When spring comes, the gardener, by planting the same crop in the same place, will immediately provide a new generation of contagion with his favorite food and come up with a problem for himself literally right when the plant has not even flowered. Contrary to any poisonous chemistry, every year the concentration of such harmful organisms in this area will only increase, and the only way to solve the problem is to land on this site something that the pests will not like very much. Tomatoes are among those crops whose diseases are most tenacious, because sooner or later they will have to “relocate” the bed, otherwise it will simply die.
In addition, plants, like any other living organisms, release into the environment their waste products. It is logical that such excretions cannot bring any benefit to the body, and over time, accumulating, they will increase their concentration as opposed to useful substances, which were extracted by the plant from the soil for their own vital activity. As a result, the plant has nothing to eat, but the poison around it accumulates more and more each year.
For thousands of years of serious occupation of agriculture, mankind has created technology, which was called crop rotation.
Most likely, even most avid gardeners do not know it by heart. Yes, this is not particularly necessary if you know some of the most important rules.
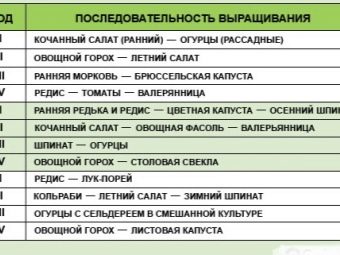
For several years in a row, not a single culture will successfully live in the same place, because the garden plantation should be changed regularly. Here it should be understood that the replacement of one plant by another, akin to the first, will not bring any particular result, since the pests and the need for certain trace elements can be very similar. Replacing the culture must be made on the one that is very different from its predecessor.
One year is almost never enough for the site to recovertherefore the plant that grew here usually does not return earlier than two years later. There are plants that require and where the big breaks, but tomatoes are not among those.
By planting a certain crop on a plot, you can already plan what will grow here next year. Some cultures provide soil and beneficial transformations - for example, they can saturate it with certain trace elements or even scare away pests and bacteria. Tomatoes have practically no outstanding benefits for the soil, but you can think about where to plant them next year. On the other hand, next to them is usually not observed an abundance of weeds, and this allows on the same bed next year to plant onions, garlic or carrots, which from such a neighborhood could die.
Most plants have different micronutrient needs, so the depletion of the soil after such sowing may be uneven. This factor should also be taken into account, because if this crop does not grow here, then the other could grow even with a relatively small fertilizer with a narrowly targeted means.
When changing places of cultivation of crops can also achieve a good harvest.
When should I change a place?
If the tomatoes in your garden are already growing, and there are no complaints about their fertility yet, it still does not mean that they are saved from the move. It may be worthwhile to change the location of the tomato bed, so that productivity increases even more. Tomatoes are not demanding to the ground - they need a well-warmed and loose earth with a significant content of loam with any acidity.
Ideally, the location of the tomato in the garden should be every year, However, it is possible to extend the period of use of the land for this particular crop to three years, if certain operations are carried out:
- change the top layer of soil, giving the former tomato garden bed radish;
- use nitrogen supplements regularly;
- plant next to tomatoes, legumes, dill and parsley;
- plant tomatoes according to the so-called Kizima method, when the root system does not branch, but goes deep into the ground due to the use of cellophane film;
- in the fall, after picking tomatoes, plant on the same bed of legumes or mustard.
Sooner or later, you still have to move the tomato plot, and the signs of such a need will be very obvious. Plants will often become ill and be subject to regular pest attacks, the number of ovaries will decrease, the fruits will become smaller. It should be noted that in greenhouse conditions such phenomena appear even more quickly and pronouncedly. If you do nothing with this, next year you can be left without your own tomatoes at all.
Tomatoes do not so much transform the soil - they do not greatly deplete reserves of trace elements, not counting nitrogen, and also only slightly oxidize it.
There are no particular restrictions on planting other crops after tomatoes. Only it is not necessary to plant there those plants that are prone to similar diseases.
At the same time the most following followers of tomato in the garden are such cultures:
- cabbage does not return the nitrogen content to the previous state, but it is not required - the vegetable grows well without it;
- peas, beans and legumes not only will they get accustomed here, but they will also re-saturate the soil with nitrogen, restoring it again for the same tomato;
- cucumbers completely indifferent to the main tomato diseases, but more demanding on the fertility of the soil, so you have to pre-fertilize it with compost;
- beets, carrots and other root crops have a much deeper root bedding, and therefore these plants feed in completely different layers of soil, not depleted by tomatoes - unless, of course, the Kizima method was used;
- onions, garlic and greens can act as "orderlies", clearing the soil of various pests left after tomato bushes, while these plants do not need a lot of nutrients;
- zucchini All kinds of varieties also grow well after tomatoes.
Since we looked at how good the crops are after the tomatoes on the plot, It is worth mentioning separately those who, in a similar situation, will frankly disappoint with their harvest:
- potatoes, eggplants and peppers, In spite of its not so identical appearance, it is very similar to tomatoes in its needs for microelements and for pests that are dangerous for them, because for them the former tomato garden will turn out to be too exhausted and infectious;
- Strawberry does not suffer from depletion of soil by tomatoes, but is subject to the effects of its main diseases;
- watermelons and melons on the contrary, they are immune to tomato diseases or pests, but they lack the beneficial elements in the soil where tomatoes used to grow.
Following the described schemes and models of planting, gardeners can preserve the fertility of the soil and at the same time get a rich harvest.
Where to plant?
As far as not every crop can be planted after a tomato, so they themselves will grow far from any part of the vegetable garden - it all depends on what was growing there before. It has already been mentioned that, for tomatoes, a fundamentally high nitrogen content in the soil, but in fact, potassium and phosphorus will also be completely superfluous.
Potatoes, peas, peppers, and eggplants are plants that actively consume the same trace elements and are also subject to the same pests. That is why it is impossible to plant tomatoes in open ground after these vegetables. Strawberries, in contrast to the same potato, have completely different needs for trace elements, but pests are too similar, which is why it is also contraindicated.
It is important to understand that crops, after which tomatoes grow very confidently, are noticeably larger than those that are contraindicated.
The planting of green onions or garlic, cabbage of any kind or cucumbers, zucchini and other melons, as well as carrots and beets, makes it possible to count on the fact that already next year you can count on an impressive crop of ripe tomatoes.
Separately, it should be said about the so-called siderats - plants that most quickly restore the right balance of substances in the soil. Such crops, in particular, are able to equalize the acidity, which after a tomato rises somewhat, while the soil often does not even need to be given a full year to move away - these plants simply land closer to autumn, when the tomato bushes are already utilized. Planting of similar plants in early spring is also permissible.
The most popular siderata include any legumes, as well as mustard. Special planting of green manure is practiced on the open ground, but it is most justified in greenhouse conditions, since greenhouses often have very limited size and orientation strictly on one culture.
If we are talking about a greenhouse, these plants are planted already with the beginning of the first frost, and you need to remember to carefully mow them about 1.5-2 weeks before the planting of new tomato bushes.
Neighboring plants
Additional complexity of crop rotation is also in the fact that the plants need to be placed in the garden, not only in the correct sequence, but in a certain order in relation to each other. It would be wrong to think that the influence extends only directly to the soil of its own bed, and does not go beyond its limits. Its essence most often lies in the fact that toxins secreted by the root system of each plant can protect it (and some other cultures) from harmful organisms, but can also poison its neighbors. That is why the neighborhood in the garden can be both useful and disastrous.
Fortunately, tomatoes in terms of neighborhoods are relatively not picky. Next to them, not the most popular get along well, but numerous cultures, which may include watermelons and melons, beans and peas, pumpkin and eggplants as an example. Cabbage and leeks are also welcome, and the latter also protects tomato bushes from typical pests. You do not have to mix all these crops in a heap, because with the same pumpkin tomatoes are well combined only with relatively little contact between the plots, and problems begin with cabbage, if strawberries are found somewhere near.
But the neighbors described above will be a good barrier to separate a tomato garden bed from other crops with which tomato bushes do not get along even nearby.There are only two such crops, but they are considered critically important for any gardener - we are talking, first of all, about potatoes, as well as cucumbers.
It is also not necessary to plant strawberries nearby, because the most common disease of tomatoes, late blight, is a great danger for this crop.
There are some plants that do not get along well with almost any garden crops. There are not so many plants that are so hostile to all living things, but thickets of wormwood or black walnut or fennel growing next to the garden may be the very reason that it doesn’t make it harder to produce an impressive harvest with its fertility.
Tips
Finally, you need to tell a few tips that are somewhat out of the general rules. Compliance with such recommendations can lead to an even greater increase in yield, which will certainly please any gardener.
- Plant after tomato for faster soil recovery, However, it is recommended to pay special attention to the garden where the tomatoes infected with late blight were growing. This tomato disease is very dangerous both for this crop and for many others, including potatoes and strawberries, because the problem must be solved immediately after harvesting tomato bushes. The cultivation of legumes is considered to be the most popular way to combat infection, but mustard shows itself even better and also produces preventive measures for other diseases. In addition, even crops such as rye and winter wheat help clean the soil from contamination.
- In some cases, next to tomatoes, you should grow plants that are of particular culinary value, perhaps not carried, but help tomato bushes to solve numerous problems. For many pests, the tomato bed will be inaccessible if there are blotches of such herbs and flowers as marigolds and nasturtium, taghetis and coriander, or tansy and calendula next to it. Interestingly, basil, used as a seasoning in the preparation of numerous dishes, helps to improve the taste of tomatoes, even if it just grows close to them.
- Like most cultivated plants, tomato bushes do not tolerate strong winds very well. If the climatic conditions in the region are such that this problem cannot be avoided, tomatoes should be planted surrounded by beans or corn - this neighborhood will protect the tomatoes from strong wind and heavy rainfall.
Choosing a plot in the garden for growing tomatoes should not be forgotten that crop rotation should not interfere with the common choice as such. Tomato - a capricious plant, because it needs a place that is not deprived of sunlight and heat. At the same time, tomato bushes do not like marshy soil, needing loose soil. Otherwise, root rot and fungal infections cannot be avoided.
Alternating crops in your garden, these fundamental factors cannot be ignored, otherwise even ideally organized crop rotation will not help to improve crop yields.
Features of crop rotation in the garden, see the following video.