How to tie up tomatoes in the greenhouse?

In greenhouses and greenhouses, tomatoes can grow and bear fruit year-round.But not every gardener can grow a good crop of these vegetables. There are many ways to do this. One of them is the garter of a tomato in a greenhouse with the help of various devices.
What is it for?
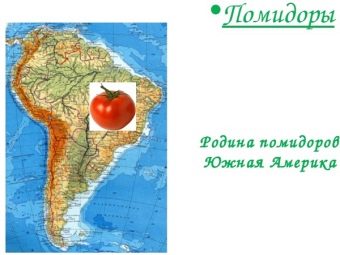
In the wild, tomatoes are not found. They relate exclusively to agricultural crops, the formation and care of which requires considerable energy consumption. Now these types of vegetables are grown both in the garden and on an industrial scale. But it was not always so. South America is traditionally considered the birthplace of tomatoes. The tribes of the Indians ate the fruits of this culture, calling them "tumatl", which later was reborn as a "tomato".
Tomatoes were brought to Europe by Columbus in 1493. To cultivate this culture began in the second half of the XVI century. In 1554, the Italian Andrea Mattioli first gave the tomato its true name “Pomi d'oro”, which means “golden apple”.
Between seeds and delicious ripe tomatoes on the table are whole months of hard work. In planting seedlings, watering, pruning and many other ways to care for vegetables have their own characteristics and nuances. Wait, that simply dropping the seeds into the ground at a certain depth, you get a countless crop, you should not. You need to arm yourself with all the necessary knowledge and subtleties, because tomatoes are a very delicate and demanding plant, requiring special treatment of planting, watering and other conditions for successful growth.
One of the most important, I can even say, the most important event of them is tying. Moreover, it is of particular importance where the tomato is tied up in open or closed ground. In greenhouse conditions, you can achieve maximum yield of vegetables. The quality of the greenhouses and the material from which they are made also influence the formation of this vegetable crop. Greenhouses are film, polycarbonate and glazed. The latter are most preferred because they are adapted for year-round cultivation of vegetables.
It is useful to know the basic rules and subtleties of tomato garters. There are many ways, each of which directly depends on the quality characteristics of this type of vegetables. Some believe that tying up tomatoes is not necessary, which directly affects the quality of its rooting and yield, and also violates the so-called natural habitat. But it is not.
The greenhouse itself is such an artificially created place in which there is both its microclimate and its own characteristics. In some places with a harsh climate, this way of growing vegetables is the only possible one.
Tie up the bushes still need. In hothouse conditions, as a rule, tall species are grown, trying to use its area in several tiers. Although, with a proper garter, good yields are yielded by low-growing types of tomatoes. Some early tomato varieties do without garters at all. The good yield of these greenhouse species provides a high rate of vegetables per unit area.
Unbound bushes have every chance to rot from the proximity of the earth or to get sick with late blight, the carrier of which lives in the soil. The affected fruits are unfit for consumption, which automatically makes every effort to grow them in vain.
Bushes and fruits of tomatoes do not tolerate the ingress of water, so only the roots are watered. It is difficult to water the lying plant, therefore it is better to tie it, otherwise you can generally lose the entire crop. Care for neat beds of vegetables is much more convenient.
Tying bushes contributes to the formation of their powerful root system, which improves the delivery of nutrients to the fruit. As you can see, there are a lot of advantages in growing tied tomatoes in a greenhouse.
Rules for the formation of bushes
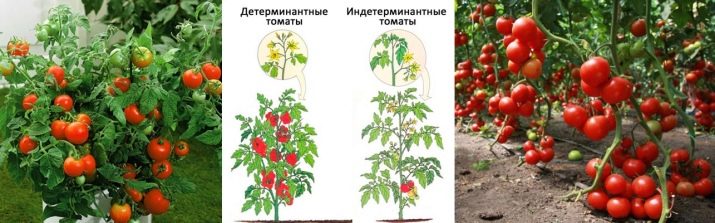
You must be able to properly form the tomato bushes in the greenhouse.This procedure is performed with tied up plants. There are determinant ones - weakly branching undersized varieties, and indeterminate ones - tomato varieties with unlimited growth. Indeterminate forms in two stalks. From the tomato bushes fixed on the trellis, 25-30 days prior to fruiting, they are planted; the top of the stem is removed.
The formation of determinant varieties and hybrids is carried out in one stem until the independent termination of growth. The main stem is cut over the fifth inflorescence, transferring the force of fruiting to the side parts of the plant. The formation of tomato bushes is impossible without the proper pasynkovaniya.
During the growth period, lateral shoots or shoots that grow from the leaf sinuses of the main stem appear in the tomato bush. If you leave them, they will eventually grow. The plant goes into the growth of the bush, and the fruit may not develop. Masking is the disposal of a plant from these unnecessary shoots. Proper staving directly depends on tomato varieties.
Cutting steps with determinant types of tomatoes should be done with care so as not to block the growth at all. It is necessary to leave one process from the sinus under one of the inflorescences of the top of the bush. He will pull the plant up. Then this stepchild is removed and a new one is formed instead.
In the hottest period, the plant forms three stalks. If it is properly stepped, such a plant will bear fruit all summer. Some types of deterministic tomatoes do not stepson and are not tied up, for example, stem and hybrid varieties. In the greenhouse, they can grow in buckets and pots, do not require special care, but bear fruit only once, then stop growth and formation.
Determinant varieties are tied up only once, forming a bush in two shoots.
Indeterminate tomato varieties will grow as long as they have enough space. Under suitable conditions and the accompanying warm climate, these varieties grow during the year, reaching a three-meter height. The bush of each of them gives on average up to 50 kg of tomatoes. Bloom every three leaves. Seedlings can be planted in the ground in two months. Fruit ripening occurs after four months. This sort of tomato must be pasynkovat all summer, tying up as they grow.
Determinant varieties are more difficult to reach with stepsons than indeterminant ones. The risk remains to remove the main shoot, which continues to grow the bush. The main stem of this type of tomato is completed with a special brush, and if it is removed, the plant stops growing and the possibility of fruiting.
There are basic rules for the removal of stepsons: the formation of the crown of a bush is made already after it has fully grown; stepchildren are cleaned, preferably with their hands, and this is best done in the morning, before the dew has come down. The procedure is performed in gloves.
In order not to accidentally remove the necessary stems, they are formed (rolled out) not earlier than they grow by 5 centimeters. At the same time, the necessary stem is planned in advance for the main role.
Remove the shoots as needed. In wet climates, it will be produced more often than in dry and warm weather. The operation itself is carried out in gloves and looks like this: the stepson is clamped between the fingers and, swaying to the sides, carefully breaks off. At the same time at the site of the cliff remains the wound surface, where pathogenic bacteria can enter. Therefore, the wound area is treated with any disinfectant composition until it is fully tightened.
In case you have to cut the stepsons, it is better to do it with a sharp knife or scissors quickly in order to cause the least damage to the plant. The instrument must be periodically disinfected, dropping into a weak solution of bleach or manganese. It is not completely cut off, leaving part of the shoot to avoid re-growth in this place. It must be remembered that the so-called dormant buds can hide in the axils of the trunk, and with time they can give a new escape.This is a varietal feature of some species.
Therefore, it is worthwhile to regularly examine the plants for the presence of these buds and to prevent the growth of the bush and the desolation of the beds.
Cut off the shoots should be immediately removed from the greenhouse, so that they do not begin to rot and do not become distributors of infection. Experts advise not to get rid of waste, and use their infusion to irrigate berry bushes from aphids and insects.
The skills of forming and tying up tomato bushes are necessary for obtaining a good harvest, and it is also easier to care for such plants.
Choosing a prop
It is impossible to get a good harvest from tomato bushes if you do not take care of them and not form them correctly. To do this, there are various ways and methods of binding and fixing bushes, focused on their particular development and fruiting.
First you need to decide on the choice of support, for which to study and compare all the options available today: whether it is a trellis method, which is divided into linear (vertical) and horizontal, or fastening with stakes, a fence or frame.
Fix the plant to start in a week after its landing in a closed ground. To do this, use stakes, twine and twigs - devices for supporting plants, as well as garters and special hooks, which should be soft and durable at the same time. To fix the bushes of tomatoes can not use fishing line and other similar materials, as they will fit into the stem as they grow and can cripple the plant.
Which of the methods is more effective - yet to be understood. But to know the general ways of tying everyone should know. So, gardeners traditionally use a cloth several centimeters wide as garters. To do this, take sheets or other materials, torn into small strips 10-15 cm long.
Some prefer to use capron, because it does not deteriorate in a wet environment and is suitable for multiple garters. In this case, used garter material for further use must be processed, disinfected or simply washed without the use of aggressive detergents. This is necessary so that the pathogens of infectious diseases are not transmitted from last year’s plantings of the present.
Now there are modern ways of plant garters - plastic clips. This is a good alternative to the old-fashioned way. They are inexpensive, easy to use, and you can use them for several years.
For tomato garters on a large scale, it is advisable to use a special device - a binder, the mechanism of action of which is based on the principle of the stapler fastening the stem with the support. This type is often used for fixing vineyards.
Ways
The generally accepted standards for garter tomatoes in the greenhouse does not exist. Each is determined by the choice itself, based on general recommendations on this issue.
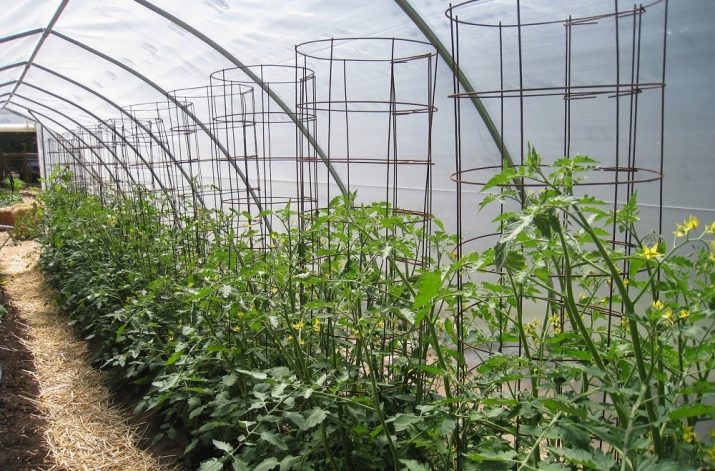
One reliable method of fixation is the linear method by tying plants to a vertical trellis.
Tying can be done using horizontal or vertical methods. For this, tapestries are formed by driving poles or wooden beams into the ground. The advantage of these methods is as follows: for the sake of increasing the harvest, you can leave a few additional stems - stepsons, and take an excellent crop of vegetables for a whole year.
One of the easiest ways to tie up tomato bushes in closed ground is to fix them with stakes: each tomato has its own stake. The role of stakes is also successfully performed by any trimming of pipes made of metal or plastic, as well as wooden sticks. Anything that is handy will do. Stakes are best placed before planting a tomato.
The peculiarity of the garter with stakes is that this method is suitable only for small plants.From the gravity of this type of support can crack and break, damaging the bush. In addition, it is necessary to carry out the garter as necessary during the entire time of growth of the bush.
A convenient method for gartering tomato bushes is a hedge. For its formation using a special plastic mesh, pulling it between the stakes on the rows of beds.
You can attach and fix the plant without garters, for example, using a frame. Such designs are made of wire, wood and plastic. They completely cover the bush and hold it. Fruit brushes as they ripen just cling to the frame. However, this method is rather inconvenient for greenhouses, because it does not allow the use of the entire productive area of space.
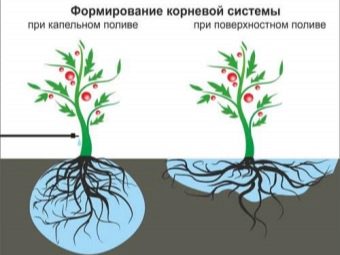
About half a century ago, engineer Igor Mikhailovich Maslov invented an innovative method for efficient cultivation of tomatoes, which allows for maximum yield. His invention is popular to this day. The method is particularly relevant in the northern areas, where the use of greenhouses for growing vegetables is the only way to produce a crop.
Maslov conducted numerous studies of various varieties of tomatoes and discovered that these plants contain unused potential, the disclosure of which to a large extent can contribute to an increase in the yield of vegetable culture.
Growth potential is enclosed in their roots and laid genetically in them, since initially this kind of vegetables grew in the forests of America, from where Columbus brought it to Europe together with potatoes and tobacco.
So a simple observation of the plant led to the discovery. The scientist determined that the evolution of this species was carried out in a different area of growth, where he was forced to survive in the special conditions of the climate, being practically in limbo. This property determined the particular structure of the root system of tomatoes. All information about this is laid in the genetic code of the plant, which retained this ability to grow roots throughout the surface of the stem. The current varieties have retained this natural feature, which is imprinted by tubercles on their main stem.
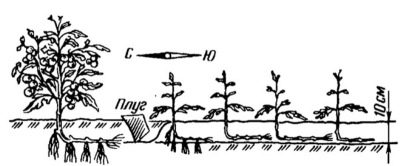
By activating these buds, roots, you can significantly improve the nutrition of the whole plant, which will positively affect its total yield tenfold. The application of the method begins at the stage of planting seedlings in the ground. This is not done in a strictly vertical position, but practically lying down. The bush is located in the land from north to south.
Before planting, the stem should be cleaned from the lower leaflets, then deeply deepen into the soil. In this case, the distance between the bushes should be maximum.
Plants according to Maslov practically do not stepchild. Grown stems bend to the ground, sprinkled with soil for 10 centimeters. Pysynki rooted and eventually become independent plants. This principle Maslov adopted from strawberries, able to multiply with the help of "whiskers". Watering according to his method should be carried out strictly under the root.
The basis of the invention Maslov formed scientific knowledge of genetics, breeding, biology, chemistry and history, as well as practical research methods in the agricultural field of crop production. His discovery marked the beginning of a new stage in the agrarian industry.
Training
Preparing for the garter of the bushes is done in a simple way: all elements of the holding structures and the garter must be assembled and prepared in advance, having been treated with a special antibacterial composition. Elements of the fixing structures are carefully processed regardless of what they consist of: wood, metal or plastic. This is done to avoid contamination of plants in contact with their elements. Moreover, it is necessary to disinfect both new and used materials.
The formation and installation of a frame for tomatoes in the greenhouse is made at the stage of preparation for planting seedlings in the ground.This is necessary to protect plants from damage that are inevitable when mounting this kind.
The nature, methods and methods of garter are directly dependent on the quality indicators of the plant itself, as well as methods of its cultivation. Therefore, it is necessary to know how to properly use the basic properties of the factors of successful growth - water, heat and light. For high productivity in the greenhouse, it is necessary to create conditions under which the mass of fruits would be five times the mass of greens. This is achieved by proper maintenance of the hydrothermal regime and the formation of a microclimate.
It is necessary to prepare the land for planting indoors, starting from autumn, fertilizing it with organic substances, achieving its weakly alkaline composition. Tomato sprouts seated in a moderately warm land. To avoid stretching the plant to growth, it is important to control the balanced temperature of the air and the soil. Do not allow the ground to be warmed up more than the air.
Too high ambient temperature contributes to the stretching of the bushes, so you need to adhere to the temperature range of 16-20 degrees Celsius. By providing good lighting, you can avoid the extra cost of processing unnecessary processes. Carrying out photosynthesis in full, tomatoes do not grow.
Infrared radiation is the best factor for the proper growth and development of vegetables.
Humidity of air and soil are important for the preparation and cultivation of plants. In polycarbonate greenhouses, humidity is always high due to condensation, so you need to take care of normal ventilation. Tomatoes tolerate drafts well. In the design of the greenhouse it is necessary to provide lateral ventilation. Providing a balanced watering of plants, you can achieve good yields.
To avoid the formation of rot on the fruits in greenhouses, you need to use the subsoil and drip irrigation methods, as well as irrigation of the grooves. Watering is carried out at the root. To prevent the formation of a crust bushes is recommended to constantly spud. Water temperature during irrigation should be at least 20 degrees. Fertilizing every two weeks with fertilizer helps to strengthen the plant and its yield.
Applying knowledge of the natural factors of water, heat and light in greenhouse conditions, it is possible to achieve the maximum productivity of tomato vegetable culture.
Instruction
Tying up vegetables, you need to follow the instructions. For each method it has its own. So, by the vertical method, you first need to build a trellis. This is done simply. Above the beds under the roof, parallel threads of wire are drawn: left and right. Then a string is attached to the lower part of the bush, the end of which is attached to the wire. As a result, vertical strings-clamps are formed, to which the stems of plants are fixed.
The binding is carried out in a staggered manner: one bush is tied to the left wire, the other to the right one. This significantly increases the surface area for access of sunlight, which allows maximum use of greenhouse space and ensures high yield of this type of plants. Fruits-brushes are tied with special clamps. With the formation and growth of the bush, the tapestries are tightened.
Tying on the horizontal method is carried out as follows: beams are driven into rows through short distances, into which the string is stretched every 30-40 centimeters. Tomato bushes are fixed as needed on these devices.
Every week, the regrown parts of a tomato are neatly and correctly tied up, wrapping around the trellis with revolutions every two knots with the help of special tools, such as plastic clips or twine.
Tying should start with the stem, protecting it from breaking.This will contribute to the stability of the plant relative to the axis of growth and will allow it to withstand the fruit load.
When tying with stakes, each peg is firmly fixed into the ground at some depth next to each bush. It should protrude above the top edge of the bushes by an average of 30 centimeters. Then the stem of the plant is tied with any of the materials, the ends of which cross and fix on the support. So that the bush does not break under the weight of a tomato, they are also tied or fastened with hooks. To fix a tomato using a grid you need only a few stakes. The joints are fixed with ordinary wire. The stems of the plant are attached to the grid with pieces of cloth, twine or clips. Fastening with wire hooks is made along the entire length of the row with a taut rope.
Hooks are pre-made from wire or rubber.
Over each plant is pulled a cable made of any synthetic material with loops at a short distance from each other. These loops are designed for hooks on which clusters of tomatoes are attached. It is done this way: a rubber twine in the form of a ring is pushed under the plant or fruit brush, the ends of which are bent and tied, fixing themselves with hooks. Subsequent similar procedures are carried out with the growth of the bush up the rings.
Useful tips
There are some simple rules on how best to fix tomatoes in the greenhouse with the help of a garter:
- The first garter of the bushes is desirable to produce immediately after planting in the ground, so as not to damage the formed bush later, which adversely affects the further development and fruiting of the plant.
- The garter process must be carried out as the tomato bush grows. The second garter to hold, without waiting until the stem begins to deform.
- When fixing the bunch with large fruits, there is a danger of damaging the stem of the plant. Specialists-gardeners use as a suspension part of the rubber in three millimeters, for example, from the bicycle chamber.
- Before using rag strips for garter of tomato bushes, it is best to soak a weak solution of manganese. This procedure does not take much time, but protects the plant from infection.
- A protective barrier against microorganisms, insects and bacteria is created in the greenhouse by processing the framework to which the tomatoes are attached.
- Fix the fruits of the plant should be avoiding contact with the ground. The plant bush should be firmly fixed to the support so that the stem does not bend.
- Even stunted bushes should be tied up. This will strengthen their root structure and contribute to higher yields.
- Using a rope for tying should make sure that it will not dig into the stalks and do not injure them.
By practicing these tips, you can greatly facilitate the care of plants during growth and fruiting, as well as get a good harvest tomato.
Five ways to garter tomatoes, see the following video.