Indeterminate varieties of tomatoes: what it is and how to grow them?

Experienced gardeners do not have difficulty deciphering incomprehensible words on a bag of seeds, which cannot be said about novice home gardeners. As a rule, bright packaging with the image of ripe vegetables, indications of the ripening time, the main characteristics of plants are striking. However, few people pay attention to the incomprehensible agronomic terms "determinant" and "indeterminant". But the quality of the crop depends on the knowledge of the special definitions.
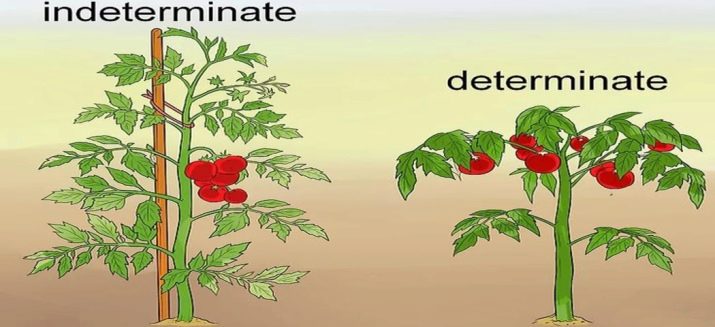
These terms are necessary when choosing seeds and denote the type of plant growth - tall or short. Determinant varieties, increasing a certain number of brushes, stop growing, and then begin to bear fruit. Indeterminate are unlimited in growth, and in the southern regions the height of the bush can reach 4 m.
It is necessary to take into account such nuances in order to plant the bushes at the optimum distance from each other, not to thicken the plantings, to properly conduct the pinching, forming the bush.
Characteristic
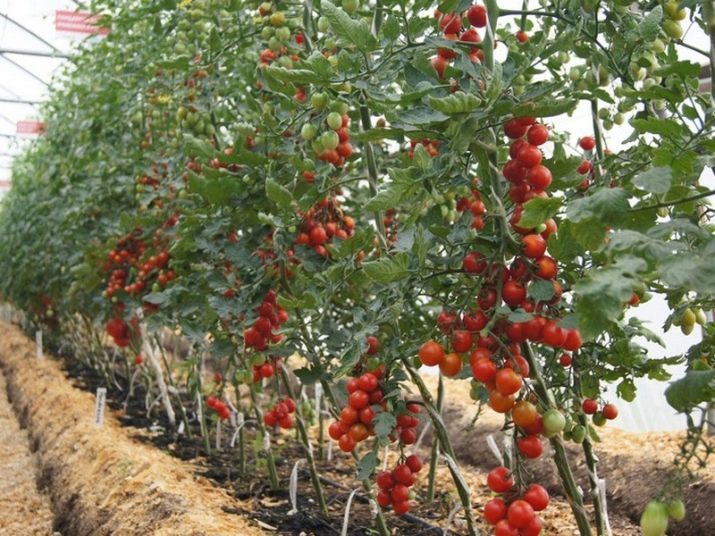
The indeterminate variety of tomatoes is limited in growth only by the duration of the warm season. Some tomatoes of this type may resemble a vine, which is not a hindrance even the greenhouse ceiling. With such a characteristic, tall varieties are best placed in the middle of the greenhouse area in order to give maximum space for growth.
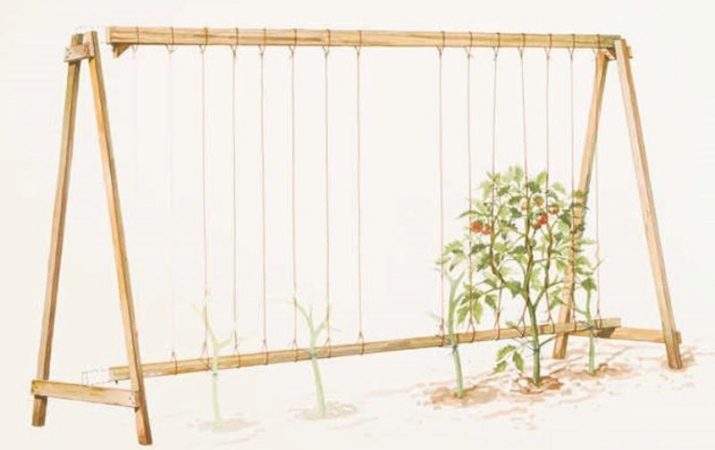
The variety needs a mandatory garter, otherwise the stem will rest on the ground under the weight of the fruit. Some gardeners are advised to have indeterminate tomato bushes on the trellis, according to the method of growing climbing cucumbers. In this case, you can expect the appearance of fruit along the entire length of the stem.
Since indeterminate tomatoes are very thermophilic, they are not grown on open ground. This is especially true of central Russia and the northern regions. But for the greenhouse, they are ideal - due to their height, they get enough sunlight and do not block the aisles. When caring for this variety, it is important to prevent the expansion in breadth, not to increase the green mass.
Tall varieties are capricious and need careful care, prone to common diseases. For example, in the central and northern regions, they often become victims of phytophtoras, which infect plants with insufficient sunlight and high humidity.
In a hot dry summer, up to 20 kg of fruits can be obtained from a bush of tomatoes of this variety, if you carefully follow all the rules of cultivation and systematically monitor the growth of plants.
What is different from the determinant?
What tomatoes are preferable, choose based on the climatic features of the region, the height of the greenhouse or greenhouse. The difference is that the determinant varieties of tomatoes are less whimsical, take root well and bear fruit even on open ground, are less susceptible to tomato diseases, tolerate forced drought, or, conversely, increased humidity.
In cool climates, it is better to choose determinant varieties. They have enough short summer to give a full harvest, and they can grow in low greenhouses under lutrasil.
Despite these clear advantages in cultivation, determinant varieties are not very popular - gardeners prefer quantitative planting of indeterminate tomatoes. The explanation lies in the increased fruiting of the latter, and hence in a more abundant harvest.
With proper care, tall varieties of tomatoes, even in the northern regions, can grow up to 3 meters and produce a crop of 12–16 kg per m2. But sredneroslye varieties under the most ideal conditions will not give more than 7-9 kg. Low-growing (dwarf, or standard) tomatoes are able to please the owners with small fruits with a total weight of 1-3 kg for the entire season.
If for some reason the variety is not indicated on the package with seeds or you buy seedlings on the market, then it is sufficient to distinguish indeterminate tomatoes from other varieties simply by the plant itself.
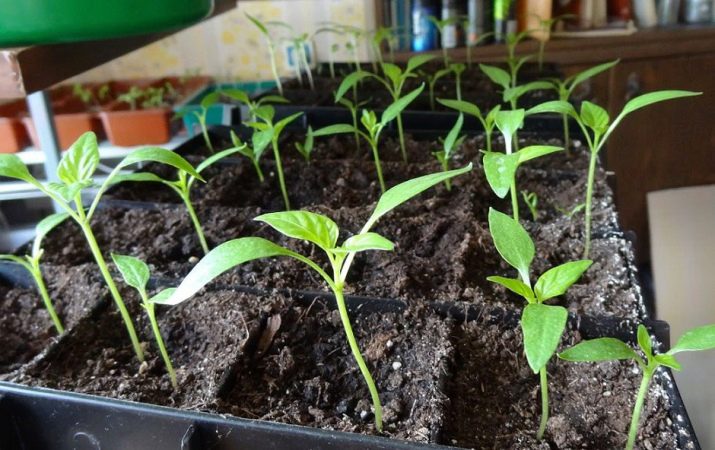
Seedlings
As soon as the sprout is pecked from a seed and appears on the surface of the soil, it forms a cotyledon knee, that is, the first two leaves on the stem. In low-growing tomatoes, the height of the seed knee will be 1-3 cm, whereas in tall tomatoes it will be much higher - 3-5 cm. At an early stage of germination, it is possible to make a mistake with measuring the length of the stem, because if the plant does not have enough light, it can simply stretch out
Seedling
In cases of purchase of unknown seedlings or in case of doubts in the variety, it is easy to determine the type of growth by the already formed small bush. Look at the plant: indeterminate variety forms the first flower brush after 8-9 of this (not cotyledonous) leaf, in contrast to the determinant ones, in which floral brushes appear below 7 of this leaf.
Adult bushes
At the stage of plants already planted and preparing to bear fruit, of course, it is too late to determine the variety for the purpose of transplanting to a more advantageous place. But this will allow you to be more careful when buying seeds and better plan your place in the next garden season. Tall tomatoes lay floral brushes no less than three leaves, and undersized bookmark brushes always occurs through one or two true leaves.
Another difference in adult plants is the final ovary, which can be observed at the top of the determinant shrub. It shows that the plant is fully formed and will not grow further. However, if a tall shrub was pinned (pinched) immediately behind the flower brush on top, then it mistakenly seems that the plant itself has stopped growing.
Therefore, to accurately determine the experienced gardeners advised to count the number of leaves between floral brushes.
Advantages and disadvantages
It is possible to determine which variety is suitable for cultivation in your area by familiarizing yourself with the main advantages and disadvantages of tall and short growing tomatoes. The undoubted advantages of indeterminant varieties include:
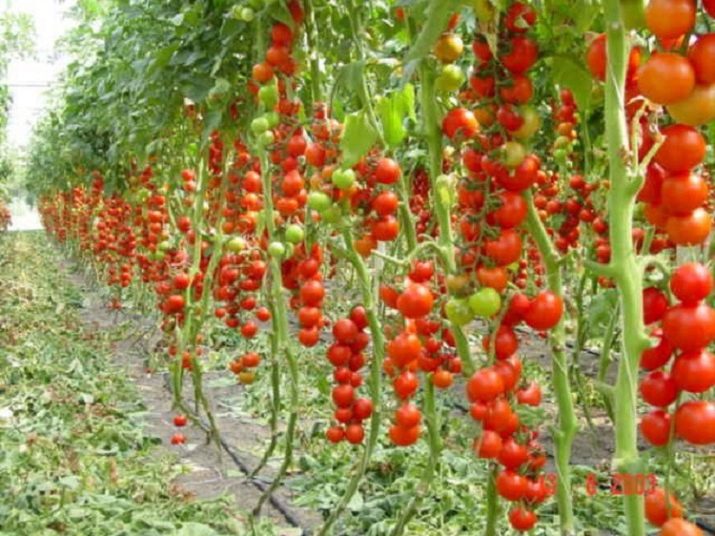
- Harvest, much higher than that which can be obtained from low-growing counterparts. The ovaries are formed along the entire length of the plant and in total can give 16-20 kg of fruit from a bush over the summer.
- Fruiting, stretched for the entire garden season. Fruits can ripen until October. In the southern regions, fruiting does not stop the entire velvet season.
- Compact beds. High growth and the need to remove the lower branches allow a more rational use of the soil space, do not thicken the beds with green mass.
Tall tomatoes have their drawbacks:
- In contrast to the undersized, they begin to ripen a month and a half later than their analogues.
- More susceptible to common diseases of tomatoes. Vulnerable to late blight, fungus and viral diseases.
- They require careful maintenance, fear drafts and lower temperatures. Therefore, in the northern areas on the open field there is always a risk of losing part of the crop. Grown mainly in greenhouses.
Growing points
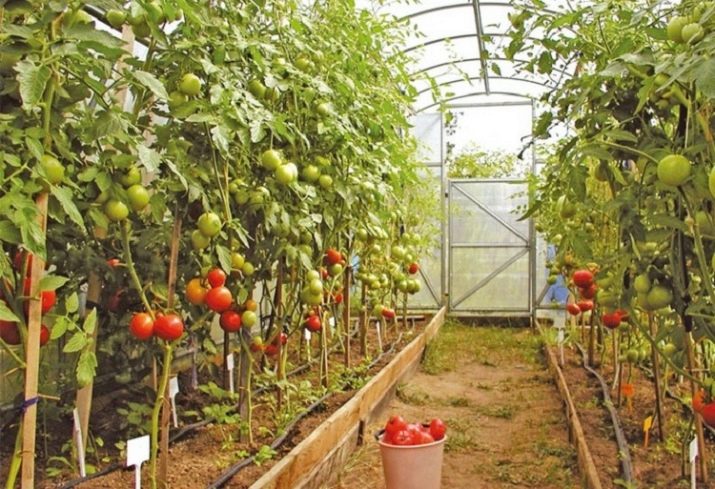
In order to get a rich harvest and to a minimum reduce the risk of tomato diseases, you must follow the basic rules of agricultural engineering. First of all, tall varieties will need ample space in height. We'll have to immediately abandon the low greenhouses and prepare a high-grade high greenhouse.
Already before planting the seedlings, a trellis or an agricultural grid is installed in the greenhouse, and the top methods of plant garter are thought out. Indentations are rapidly growing, and if you install the suspenders later, you can damage the plants.
Bushes are planted at a distance of 70 cm from each other, given the future size of the plant.The gap between the beds should be at least a meter, which will simplify the care of tomatoes and delimit the space of the greenhouse.
Formation
Tall varieties need to be formed, leaving one or two main stems that will serve as central trunks. Be sure to clean the stepchildren at the stage of their germination, it is very important to prevent thickening of the bush.
The lower leaves are cut when the plant is old enough. Excess greens are removed to ensure that the bush gave all its strength to the formation of floral brushes and fruits. It is also important that the overgrown branches do not interfere with the ventilation and access of sunlight.
Toward the end of summer, when the bush reaches the greenhouse dome, the top is pinched to stop growth and direct the energy of the plant to the ripening of the fruit.
Watering
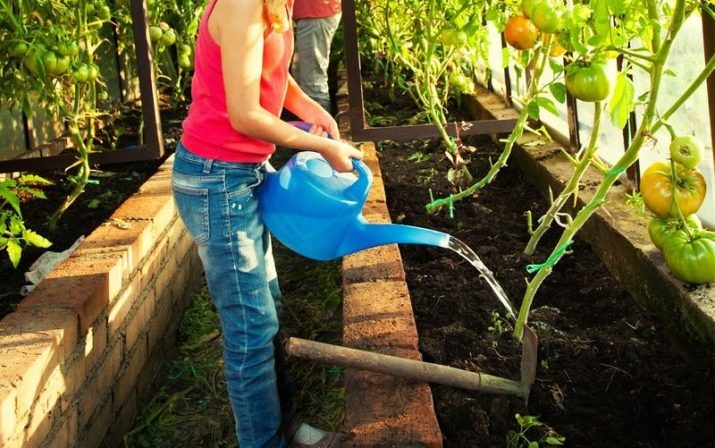
Watering is done on time. The frequency of irrigation depends on the weather and soil composition. It is important not to let the ground become completely dry, but it is absolutely impossible to pour tomatoes too. The best option is plentiful watering of tomatoes every 5-7 days. Watering plants should be at the root so that water does not fall on the leaves, otherwise the risk of disease of tomatoes is high, and on hot days and sunburn. Water the bushes should be warm water early in the morning or in the evening, when the sun is less active.
Top dressing
Make basic fertilizers at least three times per season:
- 10-15 days after planting bushes in the ground;
- during flowering;
- after ripening of the first fruits.
There are countless ways of feeding, and each gardener experimentally selects his own, suitable for the quality of the crop and the presence of feeding elements (manure, chicken manure, organic infusions). In addition, commercially available mass of complex mineral fertilizers, ready to use, you just need to follow the instructions.
Diseases and pests
Even with the most careful care and ideal conditions there is a risk of losing the crop due to diseases or pests that are susceptible to tomato plants. The main problem is that in the early stages it is impossible to determine the symptoms of the disease, or the larvae of the pests lurk deep in the soil. To prevent such misfortunes, experienced gardeners use prophylactic drugs, already knowing exactly what ailments tomatoes are in their area. Among the most common diseases are the following.
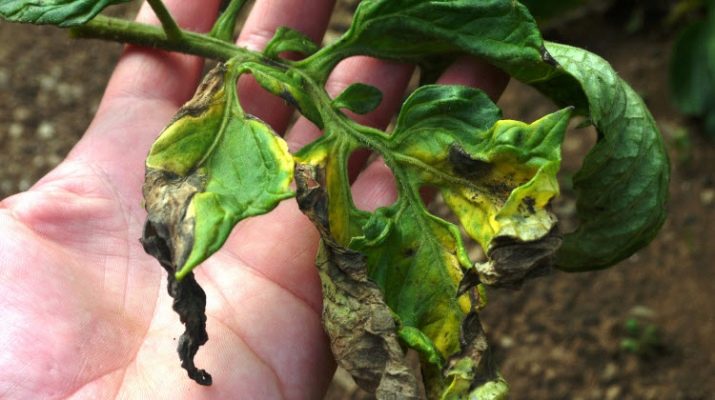
Late blight
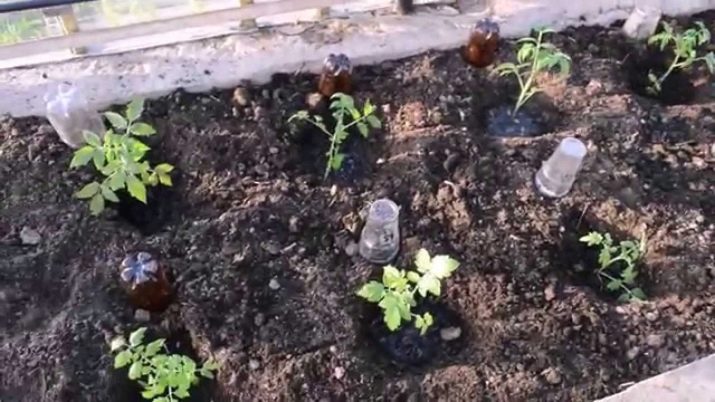
Fungal disease that destroys the leaves and stems, and then the fruit. It is characterized by the appearance of brown spots, spreads at high humidity and low temperatures. To prevent it, tomatoes should be sprayed with the prophylactic drug Fitosporin-M, aerated the greenhouse, preventing condensation on the walls.
Water the tomatoes strictly under the root or through an inverted plastic bottle buried in the ground.
Mosaic
Viral disease manifested by yellow spots on the leaves, twisting and wilting of plants. The diseased plant must be removed from the root to prevent the spread of the disease to neighboring bushes and to preserve the crop. As a preventive measure, tomatoes are sprayed with iodine solution at the rate of 10 ml per 10 liters of water.
Rot
The disease has different forms: brown rot (around the stem), gray (mold on fruits and leaves in round ulcers), root (damages the root neck) and apical (black spots appear on immature fruits). Tomatoes are susceptible to any form of disease in rainy and cold summers.
In order to prevent, it is necessary to spray the plants with Fitosporin-M, to raise the temperature in the greenhouse, if possible, to reduce the frequency and volume of irrigation.
Not less damage to the crop and bring insect pests, devouring plants and laying eggs in the soil. These include the following.
Spider mite
The insect has microscopic size and light color, so it is difficult to notice. Sucks the sap of the plant and turns the leaves around with a thin web.Prefers dry air and lack of drafts. Regularly check the lower part of the foliage of tomatoes for black spots, aerate the greenhouse and do not let the soil dry out. If black spots are detected, the bushes should be sprayed with the preparation "Fitoverm".
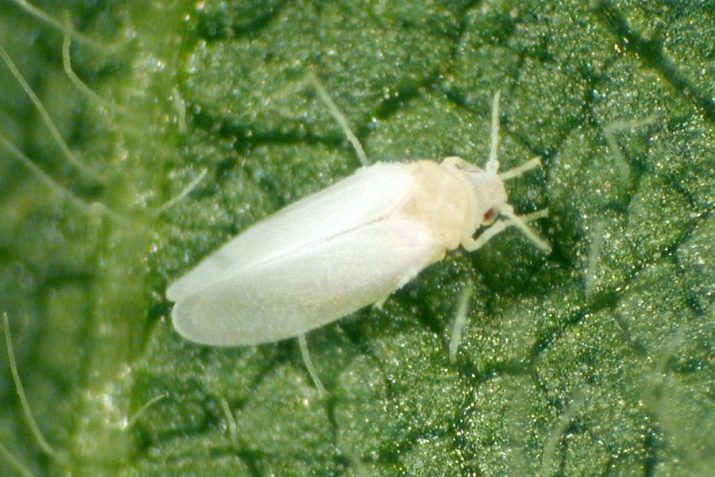
White fly
Centimeter insect with white wings. Damage to plants, laying the larvae under the leaves. It feeds on juices, in the process of vital activity of the larvae a black fungal plaque appears on the leaves.
When an insect appears, the bushes are sprayed with "Phosbecid" or "Tsitkor".
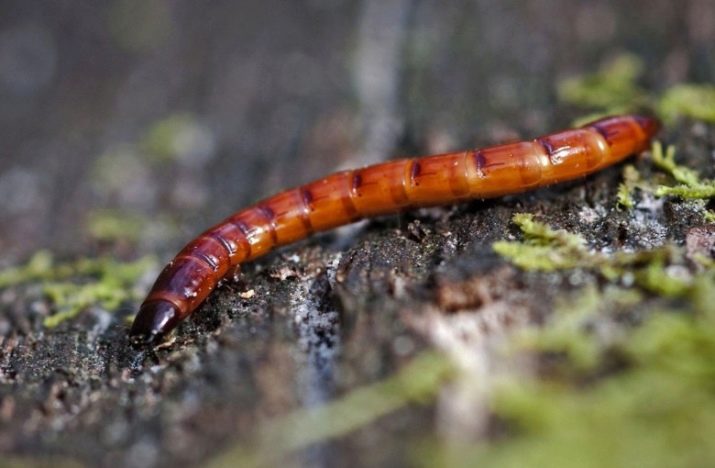
Wireworm
Yellow caterpillars feed on the roots and stems of tomatoes, capable of destroying the plant before the fruit begins to ripen. Prevention is carried out in the spring, a week before planting, digging into the soil pieces of vegetables on long skewers. After a few days, the skewers are pulled out and checked for the presence of potholes and strokes in the vegetables. If any, the soil must be treated with the drug "Basudin" or its analogues.
Tips from experienced gardeners
Each gardener has his own little secrets for growing certain crops. Mastery comes with experience that they happily share with novice gardeners. The proposed tips can be used individually depending on the composition of the soil, the growing climate, your own knowledge and preferences, but they definitely will not hurt for experience:
- In one greenhouse it is best to grow several varieties of tomatoes at once - high and short, early ripening and those that will bear fruit before the first frost. This will allow to make secure in case of unsuccessful variety, try different tastes, orient by grades for the next year. Early ripening will provide a summer table with vitamin salads, and later varieties will ripen for autumn harvesting for the winter.
- Gotting is a must when growing tall varieties, but there are certain tricks here. Watch the plants carefully and do not allow the stepsons to grow more than 3 cm. The running stepson tightens its trunk and when it is cut off, the plant forms a bulky wound, which lasts longer and can become a site of infection.
- The following trick is used to grow large giant fruits: periodically, you need to remove some of the flowers from the plant, and remove several immature fruits from your hands, so that the others take power in themselves. The fewer fruits and flowers left on the bush, the larger the remaining fruits will be. The main thing is not to overdo it.
- Watering and feeding after planting seedlings in the first two weeks should try to minimize, otherwise you can “feed” the plant. There is a risk of delayed fruiting and even diseases of tomatoes. To determine the excess feeding can be on large flowers that appeared on the first leaves. Although the flowers promise good fruit, this is a false impression. They will take too much power from the plant, so the flowers are removed, and the cycling of dressings reduce or suspend.
- When tying tomatoes, turn the stem around the twine in the direction of the sun from east to west. This will allow the plant to naturally follow the light source. For tall tomatoes, the garters are not enough in the center, as heavy brushes with fruits will start to injure the plant. Therefore, to the central axis - twine - add the threads coming from the branches. As a result, each bush becomes like a cone or a herringbone, the fruits are open to sunlight, and the branches do not bend or break.
The difference between indeterminate and determinant varieties is described in the following video.