Features of growing vegetables

Vegetables are considered the basis of nutrition, since they contain useful minerals and vitamins that are necessary for the human body. To provide the family with natural vegetables, many gardeners prefer to grow them in their own beds. Such an occupation is fascinating, but requires certain knowledge in planting and caring for plants.
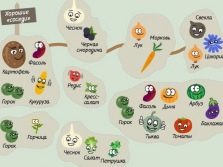
Plant compatibility
Before planting vegetables in the garden, it is important to determine which crop will be the main crop and which one will accompany it. Auxiliary plants play the role of "live" mulch, protecting the soil from drying out and weeds. In addition, a vegetable bed may include several types of vegetables, if the dacha is small. In this case, the main crop is chosen for the crop that ripens late, for example, late cabbage, and the accompanying crops are early crops (radishes or cucumbers). In order for such vegetables to fully develop and give a good harvest, it is necessary to take into account their compatibility.
- For carrots and cabbage, the ideal "neighbors" are the squash, pumpkin and zucchini. Between their rows can also be planted lettuce and onions.
- Beets, radishes and turnips are "friends" with legumes and onions. Such cultures are also allowed to combine with potatoes.
It is impossible to plan on one bed planting potatoes with cucumbers, tomatoes with cabbage, and peas with onions or garlic.
Selection and preparation of seeds
Vegetables are sown only after preliminary preparation and testing of seeds, which can be independently harvested from the best crops, or purchased at the store. Pre-sowing activities include soaking, selection, calibration and processing with biological substances. This guarantees a high percentage of plant sprouting and guarantees further excellent crop of vegetables. In the event that few seeds are required for planting, they are usually sorted manually, removing empty and damaged material.
Growing conditions
Regardless of whether it is planned to grow vegetables in an apartment, greenhouse or open field, they need to provide appropriate conditions for growth and ripening. Therefore, before sowing crops, it is important to provide adequate illumination, temperature, mineral nutrition and normal watering. Growing vegetables in the northern regions of Russia is more difficult, since there they feel a lack of heat and nutrition, and in the south of the country, gardeners have to pay more attention to watering. Today, there are many technologies through which you can artificially create optimal conditions for cultures.
Landing
Some vegetable crops can be planted in autumn, as they are cold-resistant and give good shoots in spring. For example, for the winter, radishes, spinach and garlic are recommended for planting. They are not afraid of frosts and can even be placed with flowers on the same bed. Berry and vegetable crops are planted in the suburbs and northern areas of the country in spring, in the middle and southern regions, where the winters are not too harsh, the summer residents start sowing before the winter. In the exact dates of sowing helps a special table and the lunar calendar.
In addition, the vegetables each season should be changed to the placement of the beds. The best predecessors when planting cabbage: onions, beans, turnips, tomato and potatoes. Garlic can be planted on a plot where carrots, beets and tomatoes were previously grown. Almost all root ancestors are suitable for cucumbers, except carrots.
In the greenhouse
When planting crops in greenhouses it is necessary to take into account their height, size, shade tolerance and cold resistance. Therefore, the lateral beds located on the north side can be formed with Physalis and tall tomatoes, and the center is cucumbers (it will be easier to care for them). The southern part of the greenhouse is ideal for planting eggplants and peppers. Selecting "neighbors", you should pay attention to their branching, and combine the beds should be so that the leaves of the bushes of different plants do not touch each other.
In the case when the greenhouse has a width of more than 2.5 meters, the beds are formed up to 90 cm wide. Plants that are demanding frequent ventilation are placed along the edges of the greenhouse and light-loving ones along the edges on the south side of the structure. On mixed beds it is allowed to plant no more than five plants at the same time.
In open ground
Vegetables are planted on open ground mainly in late autumn, when the night temperature reaches a temperature close to zero. Pre-winter sowing has many advantages, as the seeds are hardened and acquire endurance. Only swollen seeds are sown in open ground, they should not be germinated, otherwise they will die. As for the seedlings, it can be grown all year round in heated greenhouses, but the landing at the opening of the beds is carried out only in the spring.
Care
After planting vegetables in the country or at home on a windowsill, it is important for them to provide proper care. The soil should always be clean from weeds, pests and parasites. For this, it is not only treated with special means, but also supplemented with various microelements that stimulate growth and fruiting. For growing plants at home should be selected fertile soil with the presence of nutrients. Periodically in the soil make fertilizing fertilizer.
It is also important to take into account the compatibility of crops in soil, because some like acidic soil, while others do not tolerate even weak acidification. The list of vegetables that love sour soil is small. These are carrots, turnips, cucumbers, potatoes and tomatoes. In addition, the soil should be loosened so that the moisture is well absorbed and held.
Watering
Caring for vegetables provides timely and regular watering. “Water treatments” are best performed in the morning or in the evening when there are no bright rays of the sun. In this case, morning watering is preferable in cool and cloudy weather, and evening - in the heat. To check the level of humidity, it is enough to stick a dry stick into the ground, a normal indicator is considered to be the depth of moisture from 15 to 30 cm. Plants that already have a well-formed root system can be reduced to watering once every 3 days.
Fertilizer
All vegetables are demanding to feed, as it depends on their growth and yield. Fertilize plants need 2 times - during the formation of the root system and the development of fruits. Top dressing can be liquid or dry. At the same time, mineral fertilizers must be alternated with organic ones. Feeding is usually stopped a month before harvesting.
Early vegetables consume a lot of nutrients, so it is important for them to contribute huge amounts of potassium and nitrogen. Cucumbers are considered the most capricious, they should be fed every two weeks. Tomatoes need phosphorus, carrots need potash fertilizers and superphosphate, and beets prefer boron and sodium.
Collection and storage
Mass harvesting of vegetables, as a rule, begins in late August. Therefore, if such vegetables as peppers, carrots, zucchini, cabbage, eggplants and potatoes grow on the beds, then you need to prepare for the collection of them in advance and ensure the fruit has proper storage conditions. Since each vegetable has its own shelf life, some fruits can be stored all winter in the cellars, while others are only suitable for canning. This must be taken into account when preparing for harvesting.
For long-term storage, it is recommended to select healthy, dense and unaffected root vegetables. They are placed in cellars or basements, lined with concrete and bricks. Not suitable for storing vegetables in places where ground water is close. The roofs of the storehouses are additionally insulated with straw and earth, especially in those areas where there are cold winters. In addition, basements must be equipped with exhaust and intake ventilation.
Harvested vegetables are placed in a box or special bins are made for them, raised 15 cm above the ground. Also, for convenience, 60 cm wide shelves can be hung in the basement.
How to grow vegetables in the ridges - boxes, see the video below.