Milk allergy: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment

Among all types of food allergies allergic reaction to milk and dairy products occupies one of the leading places. And not only children are subject to it, but also adults. In this article, we will talk about why and how this form of inadequate body reaction to the product seems to be useful and necessary, as well as how to treat and prevent allergies to milk.
Causes
An allergic reaction to milk is an inadequate perception of the milk protein by the immune system of a particular person. In other words, milk protein is perceived as foreign, immunity activates all available means and forces to neutralize the action of cow protein, which is accompanied by a certain set of symptomatic manifestations in a child or an adult.
Most often, this form of an allergic reaction occurs in children, and it is up to three years. Existing statistics show that every 12 inhabitant of the planet as a child suffered from this form of allergy. Gradually, the allergic reaction to dairy products "overgrows" and most of them disappear with age. But there are 3% of people who, even in adulthood, continue to avoid milk because their body perceives it as a hostile product.
Milk is considered one of the most useful products by people, but experienced allergists treat it very wary, knowing that milk contains about 25 antigens, each of which may well lead to a “riot” of immunity and general sensitization of the human body.
Surprising results have shown and the latest global studies of this form of an allergic reaction. And they showed that even an infant can suffer from milk protein allergies, with antigens in breast milk acting as an allergen. Previously, this was considered completely impossible.
The main reason for this allergy is the immune response to one or more antigens in the product. The human body in the course of life never encounters milk. The exception is the process of lactation in women after childbirth, but allergies in a nursing mother to their own milk have not yet been revealed in the world. The immune system of a nursing mother does not define milk protein as foreign, does not reject it, since during its production it becomes an integral part of the woman’s body.
All others who do not belong to the number of nursing mothers do not have milk in their bodies. Therefore, the product caught in the stomach, naturally breaks down into its constituent parts. Proteins in this case can be perceived by the immune system as foreign. Immunity begins to produce antibodies to them. Antibodies, accumulating, lead to sensitization, penetrating into the bloodstream. When you meet again with the allergen immunity immediately activates the already familiar to him protection system.
It is a mistake to believe that only cow's milk can cause allergies. There are also registered cases of allergy to goat's milk, and to mare, and camel. But it is a cow that is called by experts the most allergenic due to the greatest number of potential antigens in the composition.
Symptoms and diagnosis
The manifestations of milk allergy are different, but in general, both in adults and in children, the clinical picture is similar. The severity of symptoms directly depends on how much of the allergen has entered the body, how high the specific organism is sensitive to the protein of cow or other milk, what is the general state of immunity.
Most often, this form of an allergic reaction is manifested by abnormalities in the gastrointestinal tract, namely abdominal pains (in the abdomen), nausea and vomiting, diarrhea. In second place - skin manifestations.This is followed by disorders of the respiratory and autonomic disorders.
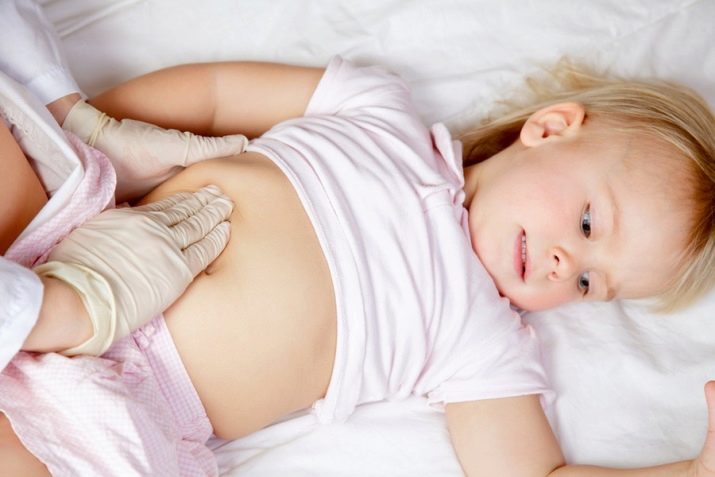
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is more common in children than in adults. In infants under the age of 1 year and in the newborn, she has the character of a diffuse, without a clear localization of pain. Since the child is too small and cannot show exactly where it hurts, the signs will be quite blurry: cry, cry, pushing the legs to the stomach, abandonment of the chest, sleep disturbance.
In this connection, many mothers often confuse the first signs of milk allergy with ordinary infant colic.
From about 2 years, the pain becomes more localized, most often it has a wave-like character and is defined in the area around the navel. The child can already show where and what bothers him. But again, rarely mothers associate such complaints with food allergies, and therefore there is a high risk that the reaction will become chronic, and this is fraught with the development of pancreatitis, cholecystitis and secondary celiac disease.
In adults, abdominal pain is usually mild, inconspicuous, and most often everything is limited to a slight pain in the stomach. Excessive accumulated in the body of an adult histamine increases the acidity of the stomach, and therefore there are unpleasant gastric manifestations. People who have been allergic to milk for years often complain of heartburn.
Vomiting and diarrhea
In childhood, vomiting is often the first symptom of an inadequate response of the body to mother or other milk. It develops, as a rule, within a few minutes after consuming the dairy treat. The more baby drank the milk, the longer and more vomiting, because with a large amount of consumed area irritation of the gastric mucosa is higher. In adults, a symptom such as vomiting is very rare.
A completely different story with diarrhea. Diarrhea is a common reaction of an adult organism to dairy foods in the presence of intolerance. But the disorder of the stool in adulthood lasts no more than a day, whereas in children the diarrhea is more severe and prolonged.
The baby can walk liquid up to 5-9 times a day, the stool looks non-uniform, with pieces of undigested food. Most often, diarrhea stops after 2-3 days (time for complete removal of milk). In infants, this symptom is most pronounced and often combined with manifestations of colitis. The feces become not only liquid, but also almost white, and mucous fragments are present in it. Severe skin irritation may occur around the anus.
If you do not help with frequent bowel movements, after a day the child may begin to suffer from dehydration.
Skin rash, itching, swelling
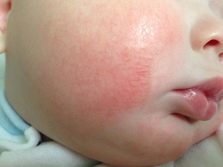
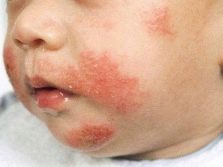
Allergic rash with milk allergy has the nature of the urticaria. Rash is mainly observed on the skin of the abdomen, back, groin and elbows. Individual blisters do not exceed 2 centimeters in diameter, rashes tend to merge and form large groups. Blisters contain serous fluid. The rash itself has a pale pink color.
In children, rashes often appear around the mouth, because the delicate skin in this area is the first to come into contact with the allergen. Such perioral eruptions are not prone to fusion, there are as separate elements.
Urticaria is very often accompanied by itching of varying degrees of intensity. Itching is associated with the effect of histamine on nerve endings. The greater the dose of the allergen, the stronger the effect on the receptors, and hence the itching will be stronger.
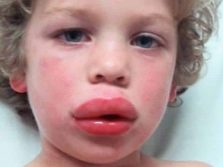
In severe cases, milk protein allergy is manifested by angioedema, which is called angioedema. It can be fatal, and therefore requires immediate emergency medical care. It develops quickly - ears, lips, eyelids, cheeks swell. Edema extends to the respiratory system, in particular, to the vocal cords. If you do not provide assistance, the glottis can close completely and the person will not be able to breathe.
Edematous tissues are very warm to the touch, and angioedema always increases from top to bottom. It helps to distinguish it from other types of allergic edema.
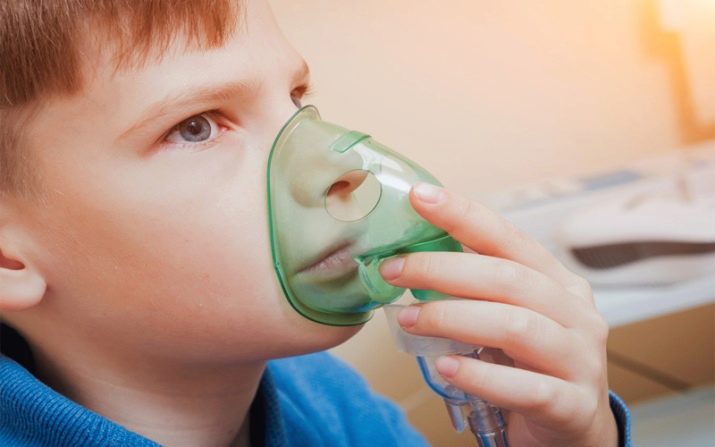
Respiratory disorders
There are almost the same frequency in both adults and children. First of all, nasal congestion may be manifested - allergic rhinitis or rhinosinusitis. Usually develops within 10-15 minutes after contact with the allergen. In adults, this time can be increased to several hours.
Dyspnea occurs infrequently and mostly only with a rapid allergic reaction.
If milk is drunk, and after a while there is a feeling of lack of air, hoarseness, shortness of breath, it is important to call an ambulance as soon as possible to prevent the development of angioedema.
Allergies in the form of coughing do not always have to cause serious concerns, and everyone knows about it. But in the case of food allergies to milk, everything is different. If a cough appeared, the edema of the respiratory organs began. It is important, as in the case of dyspnea, to urgently seek emergency medical care. It is important to remember that dry, frequent "barking" cough is especially dangerous, especially in combination with hoarseness.
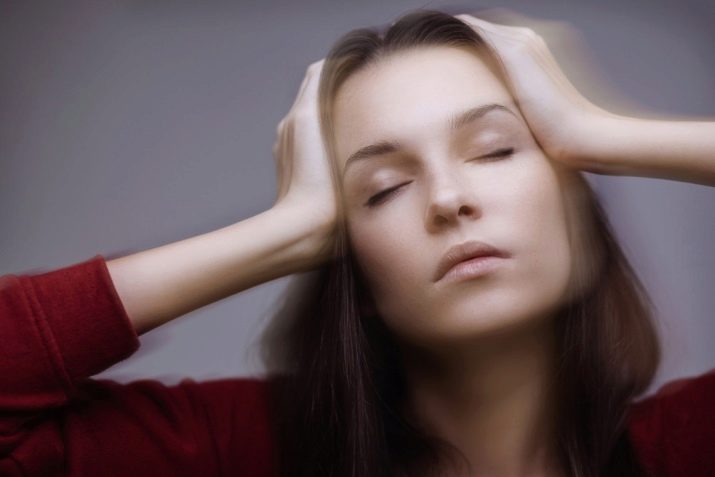
Vegetative disturbances
They are not manifestations of allergy, but they are an indicator of the compensatory mechanisms of the body, which are trying by all means to "restore order" in the system disturbed by allergies.
These disorders include rapid heartbeat, rapid breathing (not to be confused with shortness of breath!), Dizziness, loss of consciousness. Such symptoms may occur with a drop in blood pressure, with a strong sensitization.
Symptoms can be combined in random order, and can be present separately. But even with the appearance of one of them, it makes sense to be examined to make sure that what is happening is just an allergy, and not a manifestation of a different pathology. In addition, an allergic reaction to milk is completely treatable.
In the case of a child, you first need to contact a pediatrician, who can then refer the patient to an allergist. It is better for adults to make an appointment with an allergist right away - it is this specialist who knows everything about the diagnosis and treatment of milk allergy.
Primary diagnosis includes a survey and an external visual examination. Laboratory methods are also required. These include general blood and urine tests, biochemical analysis of blood, immunogram, and screening tests.
If a person has an allergy to milk, then usually in the general blood test an increased amount of leukocytes is detected, eosinophils are detected, ESR increases. In the urine may appear cylinders containing eosinophils. Biochemical analysis of blood is designed to detect an increase in immune complexes in the blood.
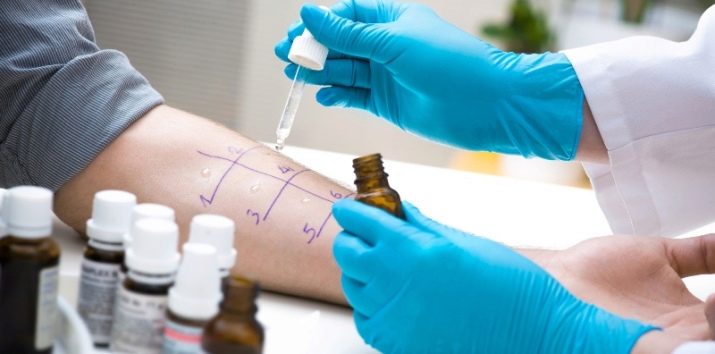
As part of the scarification test, the patient will make several scratches on the skin. They drop an estimated allergen (in this case, whey with proteins, fats, carbohydrates from the milk composition). "Guilty" antigen after a while will cause redness around the scratch, the rest will not contribute to the inflammatory process.
How is it developing?
The appearance of an inadequate reaction to milk usually proceeds in three stages, however, as with any other food and non-food allergies:
- immune stage;
- biochemical;
- symptomatic manifestations.
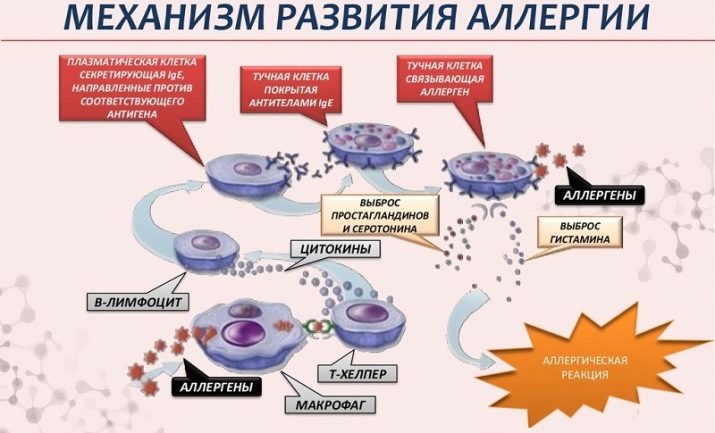
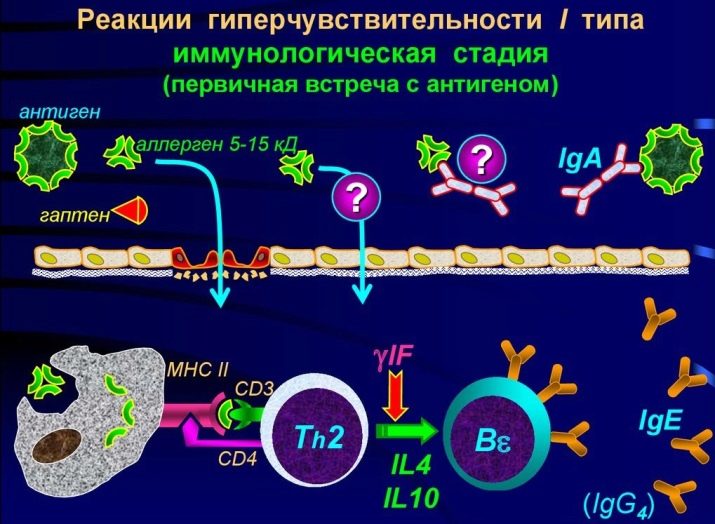
At the very beginning after taking the product in the body, that “significant meeting” of the allergen and immune cells occurs. This is the first, immune stage. Sensitization occurs. Barrier mechanisms of a healthy person (skin, saliva, gastric juice and others) are quite able to cope with most of the antigens in milk, avoiding any allergies. But if one of the mechanisms suddenly for some reason weakens or is broken, large milk molecules enter the bloodstream. There they meet the cells of the immune complex.They do not "stand on ceremony" for a long time and simply destroy foreign molecules, actually breaking them into the smallest constituent parts.
The defender cell after the massacre exposes the particles of the destroyed antigen to its own surface, thus notifying the rest of what exactly the “uninvited guest” she met. Information about this very quickly spreads throughout the body. Immune cells form a new "squad", the purpose of which is to repel the attack of dairy antigens, if they suddenly descend once more.
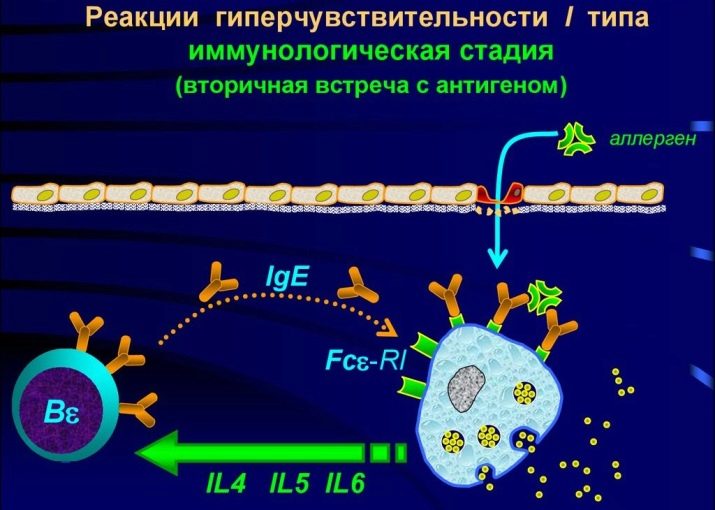
A violent immune reaction, therefore, does not manifest itself at the first, but upon repeated contact, when an entire population of “special-purpose” cells goes into the fight against the allergen.
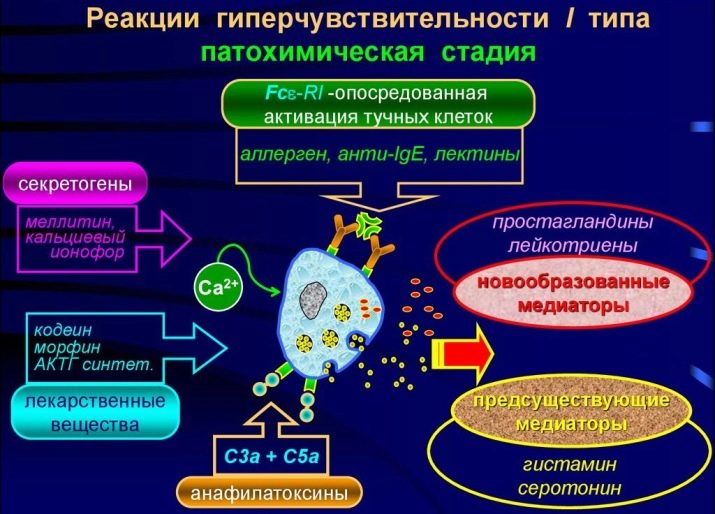
Here begins the second stage - biochemical. When an allergen is destroyed, certain substances enter the body, it is they that cause the symptoms of allergy. This is a familiar histamine, as well as serotonin and bradykinin. They are called allergy mediators. Other mediators are gradually connected to them, for example, neurotransmitters.
From this moment, the stage of clinical symptoms starts. This is a response to mediators.
Development Factors
Inadequate reaction to milk occurs not only in children. Primarily, it can also occur in an adult, even if previously he was not allergic and drank milk perfectly without consequences for his own health.
An inadequate response of the body to milk is innate and acquired. The acquired form is divided into early (in babies) and late (arising after one year old).
Most often, the provoking factors are:
- genetically inherited predisposition;
- improper nutrition of the pregnant woman during the period of carrying the baby (the presence in the diet of foods with a high degree of allergenicity);
- excessive consumption of milk in the period of gestation;
- a large number of medications that a woman took during pregnancy;
- pathological states of immunity;
- excessive innate human sensitivity to inflammatory mediators;
- various metabolic disorders.
The lack of enzymes that digest milk protein is peculiar not only to individuals, but also to entire nations. So, among the wandering northern Siberian tribes there is almost universal milk allergy. Similar inadequate reactions to the product are also demonstrated by the majority of representatives of some African tribes.
Highly allergenic products that are not recommended during pregnancy should include soybeans, eggs, milk in large quantities, peanuts, citrus fruits, strawberries, hazelnuts and some seafood, mainly crustaceans. A child with maternal blood receives not only vitamins and oxygen, but also immune cells, and therefore excessive consumption of the above products often leads to impaired immune tolerance in the fetus.
Risk factors for the development of allergies in a child under one year of age are a violation of the rules of a hypoallergenic diet during lactation by a nursing mother. It has been noticed that the child may become allergic due to late breastfeeding, as well as if the mother refuses breastfeeding in favor of adapted milk formulas.
After one year of age and in adults, this form of an allergic reaction often develops primarily (that is, for the first time) because of:
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- liver ailments;
- the presence of parasites and worm infestations in the intestine;
- receiving immunostimulants;
- adverse environmental conditions in the area where the person lives;
- excess vitamins in the body.
In this case, the leading position - in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, because it is the first barrier to milk.
Treatment
As already mentioned, this form of inadequate immune response is considered curable. But for this you need to work on your own lifestyle, completely eliminating the specified product from the diet.There is a high probability that a childhood allergy will pass with time, the child will “grow out” of it. Outside contact with the allergen, treatment courses for prophylaxis should be carried out. How many times a year, determines the doctor.
In the acute stage (if the allergy has already begun and the symptoms are present), the person definitely needs symptomatic treatment and a hypoallergenic diet. Clinical recommendations in this case may be different, as well as the choice of drug. It all depends on the age of the patient and the specific symptoms.
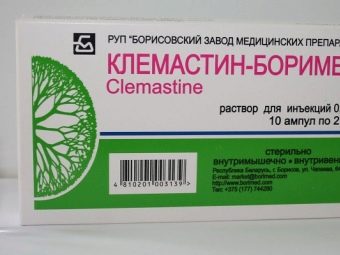
Most often for the treatment of adults and children use antihistamines: "Loratadin", "Fenistil" (gel), "Suprastin", "Clemastin". These drugs help to cope with a large group of symptoms. In some cases, shown to receive systemic corticosteroids - "Dexamethasone".
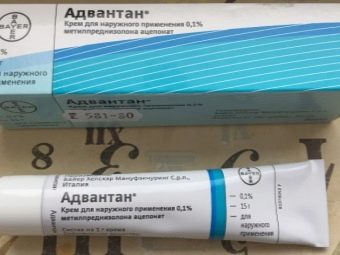
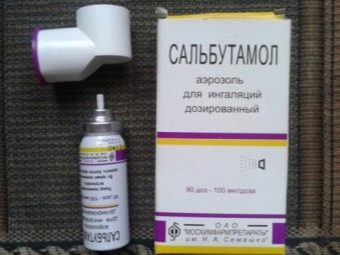
Rash and puffiness on the skin go well with the use of local corticosteroid drugs, for example, "Advantana". Allergic rhinitis sometimes requires the use of xylometazoline nasal drops. When reactions from the respiratory system provide first aid, and then prescribed "Salbutamol" or "Eufillin."
If there are disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, symptomatic remedies are recommended - “Loperamide” for diarrhea, enzyme preparations for nausea and stomach pains, “Zeercal” for vomiting.
The specific drug must be prescribed by the doctor, self-treatment is absolutely unacceptable!
At the beginning of the last century, allergies were tried to be treated according to the “similar to similar” method — concentrated solutions of the allergen were injected intravenously. But the method was found to be very dangerous for the patients because of the frequent cases of anaphylactic shock. From him today refused. But there is another method that is successfully used today. It is called the method Frequently. When it is allergic, he regularly receives a solution containing the allergen, but in a small dose, which allows him to weakly provoke immunity. Gradually, the dose increases. And so on until a person can take a pure product without any problems.
Whether to treat allergies in this way is up to the patient. In fact, the product is not considered vital, and it is quite possible to do without it in everyday life.
Prevention
The best prevention of relapse is the lack of dairy food in the diet. If we are talking about an infant, then after consultation with a pediatrician, you should choose a hypoallergenic lactose-free milk formula.
As for the general prevention in the sense of avoiding allergies, even in its primary form, a pregnant woman should take care of this during the period of carrying her baby.
So that the child does not have an increased risk of a negative reaction to dairy products, it is necessary to organize your own diet in the right way even during pregnancy.
Drinking milk is recommended to the future mother no more than twice a week in a glass. Calcium, for which pregnant and absorb dairy products, can be obtained from other products, for example, from fresh herbs and fish. In extreme cases, there are calcium supplements that the doctor may advise if there is a shortage of this element.
Eating a pregnant woman should be hypoallergenic, you can not eat citrus fruits, fast food, canned food, foods with food dyes and taste stabilizers. If you really want milk, you can drink fermented milk products - they are less likely to cause negative consequences.
Feed the newborn lure should be tailored to the individual characteristics of the child. If everyone is advised to introduce complementary foods for six months, then it is not a fact that this particular infant needs this supplement at this particular age. If the relatives of the baby have allergic reactions (whatever), then it is better to wait a little with the supplements.
It is important to monitor the health of the baby, not to leave his complaints without attention, especially with complaints of pain in the stomach, abdomen, and frequent disorders of the chair.
1-2 times a year you should take the baby to the clinic and do tests for possible presence of helminthic invasions.
From the very first minute of life in this world, the child should be attached to the breast as soon as possible. Colostrum allows you to effectively "adjust" not only the digestion, but also the immunity of the newborn baby.
A woman needs to build her own food correctly, not only during pregnancy, but also during lactation and breastfeeding. If there is no breast milk, you should carefully consider the choice of artificial milk formula. This is a question that is within the competence of the pediatrician’s doctor
Alas, a specific family cannot influence the ecology of the region of residence. But mother can quite exclude uncontrolled reception of medicines by the child at children's age. The rule here is one - any pill can be given only with permission and on the recommendation of a doctor. This is especially true of antibiotics and immunostimulants that activate the immune system. It is these drugs in our country that mothers love to give children with colds completely uncontrollably, following the calls of commercials.
Allergists emphasize that for the prevention of a negative immune reaction, psychological state is of great importance. Under stress, barrier protective mechanisms are reduced, which in itself can be the root cause of the development of an allergy.
The story of an expert about milk allergy and lactose intolerance see in the video below.