All about growing raspberries: a lot doesn’t mean difficult

Both adults and children love to eat raspberries - they are juicy, sweet and healthy. If you are the owner of a summer cottage or a small vegetable garden, then you will not be able to grow several fruit-bearing shrubs. It is enough to know the basic rules of care, to trim the damaged parts in time, to apply fertilizer, to water the raspberries regularly, and to prepare the culture for winter in the fall. All this we will tell, based on the advice of experienced gardeners.
Plant description
Raspberry ordinary belongs to the Pink family. It grows in nature as wild on the banks of rivers and in forests, and is planted by summer residents as a garden culture. There are hundreds of raspberry varieties in the world, many of which were known several thousand years ago. As a garden crop, raspberries became planted in Europe in the 16th century.
It is not only a tasty berry, but also a source of vitamins, minerals and other nutrients. This plant is very unpretentious and can grow by itself, but proper care will help increase the yield of berries.
The best time of planting
Raspberries can be planted in the fall and spring. To decide when it is better to plant, you need to know that for different climatic zones, the time of planting raspberries will be different. Since autumn is long in the southern regions, an autumn planting in late September - early October is preferable. Raspberry seedlings will have time to give roots to frosts, and in the spring they will begin to grow and develop faster.
In the southern regions, spring is dry, planted bushes can enter the phase of blooming buds, and not having time to take root. As a result, the raspberry may just die. As a rule, poorly winter-hardy varieties are planted in the spring. There are also remontant varieties that bear fruit twice a year.
Spring landing method is suitable for the northern regions. Spring is wet and prolonged there, which favorably affects the survival of seedlings. But in the autumn it is not recommended to plant raspberries so that frost does not suddenly hit and the crops are not damaged.
As for central Russia, raspberries can be planted in the fall and spring. Although, if you listen to the opinion of experienced gardeners, autumn planting will give the best result. The main thing is to choose frost-resistant raspberry varieties.
Planting in spring in open field
Advantages and disadvantages
When planting raspberries in the spring at the cottage in the open field has its pros and cons. The main disadvantage is that it is difficult to fit the exact time of landing in the spring, because the year is not necessary for the year, spring can be early or late, and in different climatic zones agronomists plant raspberries at different times. Agrotechnology planting in the fall and spring is almost the same, but the degree of plant survival is different.
In the spring, the plant literally “pulls out” the nutrients from the ground, and if you miss the right period and the roots do not have time to settle down, the seedling will simply die. In addition, in spring the weather is very changeable and can give surprises in the form of frosts, as well as in the form of heat. And in the fall, as a rule, the root system manages to take root before the onset of cold weather.
Selection of seedlings
Preparation for planting in the spring and autumn occurs in different ways. For spring planting, you can use both the material that you just bought, and the one that was dug out in the fall, which has been in the refrigerator all winter. When planting seedlings keep in mind that on the same plot raspberries will grow up to 10 years, and after that the yield will drop significantly, as the soil is exhausted. Next time it will be possible to plant raspberries here only in 5 years.
Site preparation
The spring planting of raspberries requires the implementation of preliminary steps, including the selection of the right place for the raspberries.Since the land for spring planting has been fertilized since autumn, there will not be much trouble with preparation. The main thing is to remember that the choice of a well-lit area - a pledge of high yield. Therefore, cut the bushes in time so that the stems and leaves do not shade each other.
Since raspberry is suitable for light fertile soils, do not make the mistake of choosing the land where potatoes, tomatoes or peppers used to grow. But legumes or crops will be the most optimal predecessors.
Distance and depth
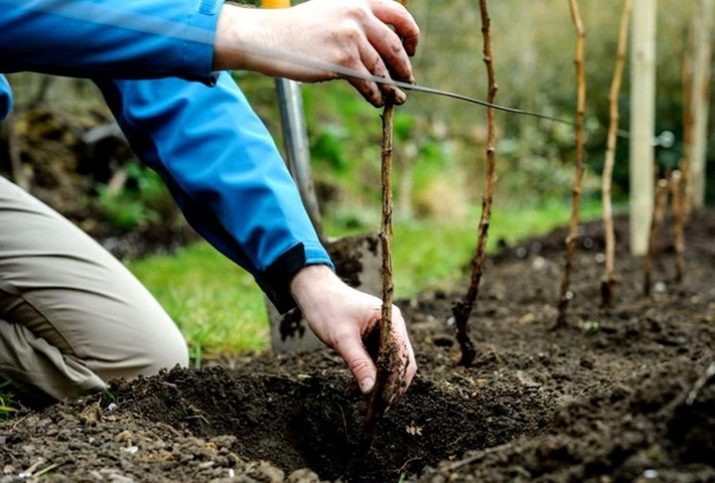
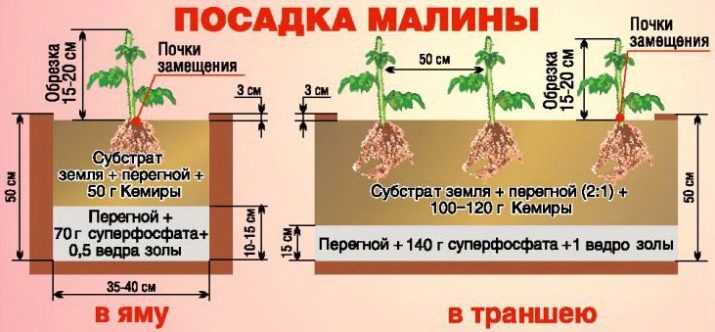
In early spring, pits of 50x40x40 cm are dug out, while the fertile layer is thrown to the side. Leave a distance of at least 50 cm between the pits, and 1.5 meters between rows. For the top layer it is necessary to ensure timely fertilization, then place a raspberry seedling in the pit, straighten the roots and fill the pit with the remnants of a mixture of fertile land with fertilizers.
Seal the top layer, make a hole around the seedling and fill it with water. At the end, fill the hole with humus and sawdust, and cut the sapling so that a “stump” 30 cm high remains. If there is no rain, water the seedlings again the next day.
Fertilization
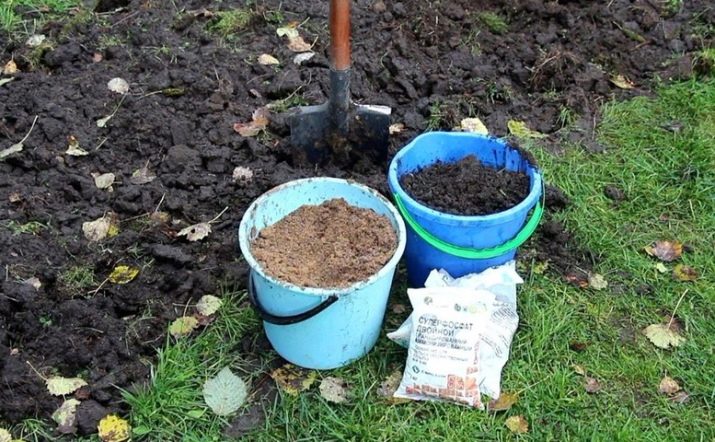
You will have to prepare the soil for spring planting in the fall (it is enough to dig up the ground and bring 2 buckets of humus to 1 square meter of land, a glass of superphosphate and potassium sulphide).
The application of artificial fertilizers in the spring is not recommended, so as not to burn the young roots of raspberry.
Ways
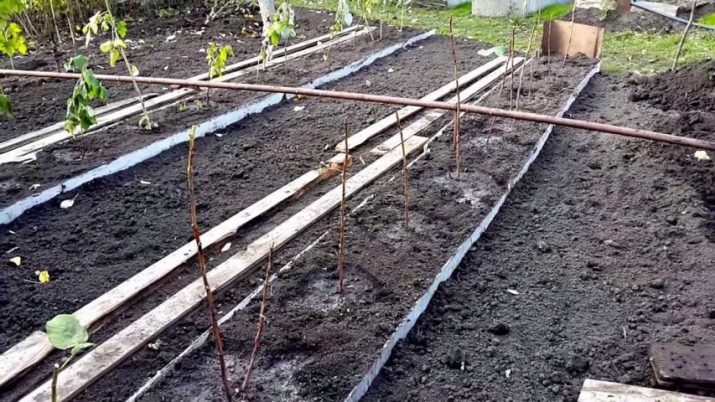
If you want to double the amount of raspberry harvested on your site, pay attention to an innovative way of growing this crop according to the method of Kurgan gardener Alexander G. Sobolev. He advises planting raspberries nesting or tape method. When nesting planting seedlings maintained a distance of 70-90 cm. The row from the row is separated by 1-1.5 meters from each other.
With the tape method, the plants are planted at a width of 40-45 cm, and the aisle is 1 meter. Thus, a strip of shoots is formed on the site. It will be necessary to thin out raspberries from time to time and replace old trunks with new ones. The main thing when growing raspberries is to prevent thickened plantings.
The main feature of the Sobolev method is the use of a two-time pruning of raspberries, which is necessary for updating the bush and, accordingly, increasing the yield. In addition, pruning helps to get rid of old and sick branches, instead of which will grow new strong shoots. We will discuss this method in more detail in the “How and when to trim” section.
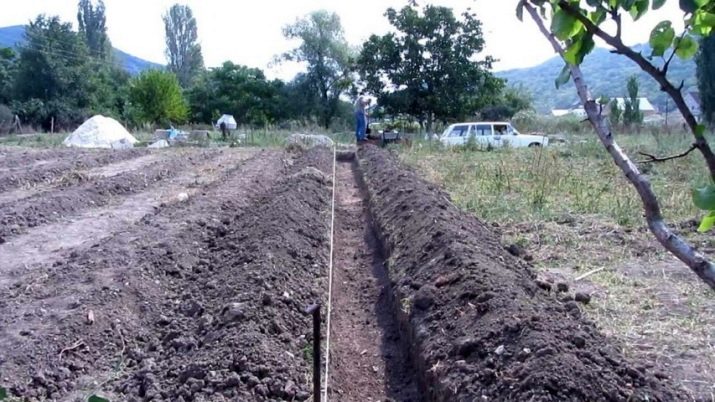
If the standard cluster method of planting is used by the majority of summer residents, then the trench method is used for industrial production or for breeding raspberries for sale. First, the plot is prepared, that is, it is cleared of stones, weeds and other waste. A trench of 50x60 cm is dug, and the aisle is 1-1.5 meters.
If groundwater is present at the site, drainage is laid out at the bottom of the trench, then the soil nutrient layer and a mixture of mineral and organic fertilizers are placed. Saplings in a trench are located about 40 cm apart. Further actions repeat the method of landing in the classic bush method.
Repair look: nuances
In the spring planting of the repair raspberry, it is necessary to prepare the soil from the autumn, dig up the soil and fertilize it. A sapling for spring planting should have an advanced root system, and the height of the shoot should be no more than 20-25 cm. The depth of the landing holes should be about 40-50 cm, and the distance between them should be 70 cm. Before planting, dip the roots in a solution of clay and black soil. and mullein.
Straighten the roots of the seedling and fill the pit with earth so that the root neck is at the level of the plot. After tamping the land, watering is performed (for each seedling, about 5 liters of water will be needed). After it is absorbed, the soil is mulched with sawdust, bark, straw, or other plant residues.
When autumn planting algorithm of actions is exactly the same, only the soil will have to prepare in the spring.
In the Volga region, Moscow region, Siberia: features
The spring planting option for raspberries is suitable for the Moscow region and Siberia, as the spring is lingering here, and gardeners have time to plant the seedlings before the start of their growing season. And in the fall, on the contrary, frosts can suddenly descend and destroy crops. For the southern regions of the Volga region and the Kuban region, it is better to choose an autumn planting, since the autumn is long and warm there. You will not only have time to slowly do all the work, but also give time to the root system of the raspberry to grow and strengthen.
For the central regions, the dates for planting raspberries are the end of March or the beginning of April. For the northern regions this is the end of April - the first decade of May. The first sign that it is time to prepare the seedlings - the beginning of the melting of the snow.
If the night temperature for several days does not fall below 5 degrees Celsius, then raspberries can be planted in open ground.
Common mistakes
A common mistake of inexperienced gardeners is a deep planting of seedlings, in fact, the roots should not be dredged more than 8 cm. If you purchased seedlings from a nursery, pay attention to the old level of soil visible on the stems and look for it.
Some summer residents in an effort to save space on the site, make narrow aisles. In fact, it is better to leave them 1.5–2 meters so that the raspberry plants do not close. As a result, the bushes will receive less of the sun, and you will lose part of the harvest.
Spring and summer care
Provided that the spring has been properly processed raspberries, in the summer you will be enough time to carry out the removal of weeds and in the case of plant disease process them with special solutions. In the usual climate of central Russia, raspberries will have plenty of natural rainfall. But if the time is particularly dry, the bushes will have to be watered every day. At the same time it is possible to add biological solutions in water for feeding and accelerated growth of plants.
In addition, you have to regularly and very carefully loosen the soil, so as not to damage the roots of the plant. For this purpose, you can also plant siderats between raspberry bushes, which not only improve the composition of the soil, but also prevent the growth of weeds.
How, when and what varieties to plant in the greenhouse?
Raspberries are a rather unpretentious plant, therefore, when it comes to growing this crop in a greenhouse, many wonder about the need for this. In fact, this is a great opportunity to significantly increase the yield of berries, as well as to protect the culture from all sorts of vagaries of nature.
Mainly in the greenhouse, gardeners grow remontant varieties of raspberry, which bears fruit twice per season. And some even manage to grow berries all year round.
This is possible if there is a well-equipped greenhouse with heating and a separate place for the mother liquor.
Here are just a few arguments for trying to plant raspberries in a greenhouse:
- fruit ripens faster and lasts until late autumn;
- the harvest will increase significantly, and the berries will be large and sweet;
- cultivation of any raspberry variety is available indoors;
- in the greenhouse, the plants will be under reliable protection from natural disasters such as hail, frost and strong wind;
- the risk of infection of bushes with pests and diseases is significantly reduced;
- you will be able to process the berries with chemical fertilizers at a minimum, and, possibly, you will do without them, respectively, the harvest will be environmentally friendly.
Optimal types for growing in the greenhouse, according to experts, are:
- "Hercules" (high-yielding variety with large berries);
- "Ruby Necklace" (excellent variety with fragrant raspberry-rich red color);
- "Apricot" (unusual variety with yellow-orange berries);
- "Morning dew" (yellow raspberry small size);
- "Bryansk divo" (high-yielding variety with large fruits);
- "Orange miracle" (has a large orange raspberry shade).
Technology
The technology of landing raspberries in a closed ground is as follows:
- we prepare the soil: we bring peat and humus into it;
- on the sapling we leave 1 shoot length of 20 cm, and cut off the rest;
- the root system is soaked in water for several hours or immersed in the mud immediately before planting;
- in the greenhouse we dig a trench 50 cm wide and 40 cm deep with a distance of 2 meters between rows and 60 cm between seedlings;
- during planting, pay attention to the fact that the root neck is flush with ground level;
- after planting soil tamp and pour water;
- If you use seedlings in pots, do not forget to provide drainage holes.
Growing methods
To grow raspberries throughout the year, summer residents use the conveyor method. It lies in the fact that seedlings are planted in January, then in March, and so every second month. In this case, the harvest of raspberries can be harvested within 2 months after planting.
Shrubs from which the harvest was harvested, pruned and left at rest. When growing raspberries in a similar way, baits and frequent replacement of bushes will be needed, and the heating of the greenhouse begins in September-October.
Caring for greenhouse raspberries includes some nuances.
- Since raspberries need a constant supply of fresh air, need to air as often as possible the greenhouse, of course, subject to warm weather. The normal temperature for the growth of this crop is about 20 degrees Celsius during the day and about 13 degrees Celsius at night. Humidity should be maintained within 65-75%. Raspberries will have to be watered 2 times a week, and once a week to loosen the earth around the roots to ensure the flow of oxygen to them.
- Soil mulching is not necessary, but desirable. As mulch is used sawdust, walnut shells, you can cover the soil with agrofibre. Feeding the raspberries will have to do 2 times a month, making nitrogen fertilizers, manure and ammonium nitrate with water. In order to pollinate flowers, it is recommended to open a greenhouse, so that bees and bumblebees penetrate there.
Harvesting
So that the raspberry berries are sweet and fragrant, the day before they are picked, the bushes stop watering. Gather raspberries in the morning every day while they are bearing fruit. Since raspberries are tender berries, they cannot be transferred from one container to another, therefore the fruits are placed in portion packs (small cardboard or plastic boxes) and placed in a refrigerator.
Greenhouse cultivation of remontant raspberries can become a serious business of a small farmer. With the right approach to the organization of the greenhouse and the care of raspberries, planting it in closed ground can bring excellent profits throughout the year.
How to plant and care in the fall?
In the autumn, it is worthwhile to start preparing a plot for raspberries one month before planting, which usually falls on the end of September - the beginning of October. They dig up the earth, freeing weeds and fertilizing with manure (3 buckets per sq. M), superphosphate (400 g per sq. M) and potassium sulfate (200 g per sq. M). And if the soil is peat, add 4 buckets of sand per square meter. m. Many gardeners prefer autumn planting, since seedlings take root better, and you can slowly prepare the plot.
Raspberry agrotechnology includes plant garter. And you can tie a raspberry according to different schemes. Temporary props will help you move more easily between rows, support the shoots with berries and greatly simplify the process of harvesting. As a support for tying berries fit T-shaped trellis made of wood or metal. Holes are made at the ends of the cross-pieces and fasten the twine, wire or agro-spaler. T-shaped supports are removed in the fall and mounted again next spring.
Transfer
Over time (after 4-6 years), the yield of raspberries decreases, so caring gardeners try to plant it. Also, this measure is necessary if the raspberry grows in the shade or ceases to bear fruit. Most amateur gardeners transplant shoots in the spring, hoping that in summer or early autumn they will be able to harvest.Raspberries are transplanted into wells 20–35 cm deep, covered with compost and covered with soil, which is tamped.
Bushes are watered at the rate of 6-8 liters per sapling. Moreover, if the terrain and soil is arid, the grooves and holes are not completely covered, leaving room for collecting water. And in overmoistened soil, raspberries are planted in raised beds, water is diverted through inter-row furrows. After transplantation, the soil is mulched with sawdust, straw, peat or dry bark.
Breeding
Raspberries are propagated by ready seedlings, layering or seeds. If you have time and enough patience, you can easily prepare seedlings from seeds at home. If you have a lamp for illumination, seeds are sown by the end of February, so that in the spring you should have tall and strong seedlings. If the seeds grow in natural light, sowing can be done in mid-March.
Boxes for seedlings are filled with a universal soil mixture. Seeds scatter on the surface, sprinkle them with another layer of soil is not necessary. The soil is watered through a sieve (for uniform distribution of moisture), covered with a film and transferred to a warm, lighted place.
As a rule, the first shoots appear after 3 weeks, but to reduce this period, you can water or process the seeds with growth stimulants.
Also among the summer residents, the methods of breeding raspberries by saplings are popular with the help of division by bushes or layings (offspring) and cuttings. The simplest way to shrub is to reproduce with lignified offspring. To do this, dig out one-year-old sons who grew up next to the mother bush. Do this carefully, trying to save the maximum number of roots.
Reproduction with green offsprings can be carried out in the spring, when they reach a height of 10-20 cm. To do this, we retreat 40 cm from the main bush in order not to damage the roots and dig out the offspring with a clod of earth.
If the raspberry stalks are affected, then a method of reproduction by root cuttings, which is carried out in spring or autumn, is suitable. We dig up the earth at a distance of about 40 cm from the bush. Dig the root of the root gently, healthy roots cut into pieces with at least 1 kidney. At the same time, fouling roots must be kept. The cuttings are planted in grooves 5-10 cm deep one by one, covered with earth and watered.
For reproduction with green cuttings take root shoots, which are cut during the thinning of raspberries. In May and June, shoots with a height of 8–15 cm are selected. They are cut to ground level and bound in 10–15 pieces are placed in a 0.1% solution of “Heteroauxin” for 16 hours. After this procedure, the cuttings are planted in a greenhouse. After 4 weeks, the cuttings put on growing in open ground.
Reproduction of raspberry by dividing the bush is used for valuable varieties, which give a small number of root suckers. When the bush is divided, the roots and 2-3 healthy shoots are left in the sapling.
How and when to trim?
Preparing plants for the winter is primarily in the correct pruning. To cut the raspberries is needed in order to increase its productivity. It is better to do pruning at the end of the summer or in the autumn, when the fruiting is complete, and the shoots gradually die off.
They should be removed at the very root, as close as possible to the ground. When pruning also remove all diseased shoots. In general, after trimming on 1 square. m. should be no more than 10-12 shoots, so that the plants get enough light. After pruning, pruned shoots are burned.
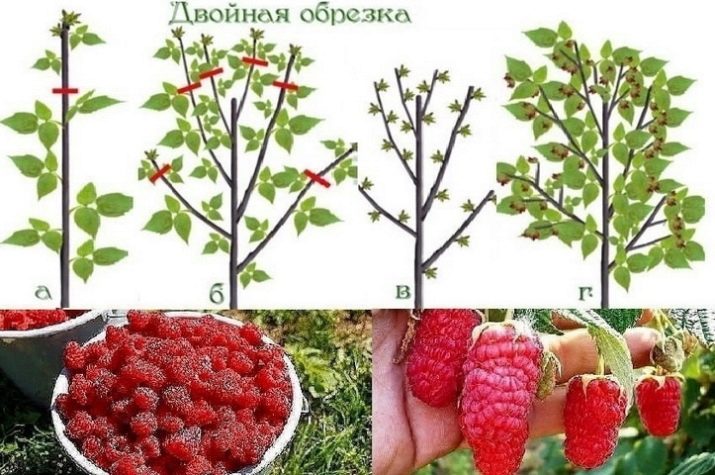
According to the Sobolev method, a double pruning of raspberries is carried out in spring and autumn. This is to ensure that the crop was several times larger than usual. Primary pruning is done before the beginning of the growing season. Shrubs leave about a meter high from the ground, and cut the tops by 10-15 cm. If before the plants had fruit only on the tips, then after such pruning all shoots and the top of the bush will bear fruit.
In fact, on each shoot you get 2-4 additional stalks.When spring pruning is important not to miss the moment: if spring came early, do pruning in May, if late - in early June. By August, new shoots reached a height of 30-80 cm and form a very lush bush.
The second pruning according to Sobolev is no less important and is done in the fall in the second year of the plant’s life. 10-15 cm is cut off not only from the top, but also from additional shoots. And by the summer form of raspberry bushes after such pruning will become like a triangle-trimmed trees. On each trimmed branch, large fruits will soon appear.
Using Soboliev's agromethod, every week you will observe the emergence of new ovaries, flowers and berries.
What is sick and how to treat?
Raspberries can be disturbed by various diseases, and every summer resident should know exactly how to carry out the treatment in order not to lose the crop.
- When fungal antraknoze on the leaves and stems appear gray spots with a purple rim. Gradually, ulcers appear on the leaves, and the greens die off.
- To combat the curliness of raspberries, when the leaves become small, tough and shriveling, the only way out is to burn the infected shrubs.
- Purple blotch often affects raspberries, causing the bushes to dry. On the stems appear purple spots that darken around the edges. It is necessary to destroy the infected shrubs, and process the rest of the raspberries Bordeaux solution.
- Mealy dew appears, as a rule, in wet weather in early summer. The shrub is covered with white bloom, the leaves dry, and the berries are deformed. In this case, raspberry is processed three times Bordeaux liquid.
Pest control
The raspberry beetle from the soil in May gets into the flowers of raspberry. When he leaves them, he damages the future fruit. You can get rid of this pest by shaking the bush. After that it is necessary to dig the soil under the bush and in the aisle to destroy the larvae. You will also have to sprinkle raspberries with “Decis”, “Confidor” or 10% solution of “Malathion”.
Stem flies, or rather, the larvae gnaw passages to the roots inside the stems, so the shoots gradually wither and rot. For the destruction of insects have under the root cut old shoots that do not bear fruit.
Aphids escape slows the development of shrubs, and leaf tolerates viral diseases. It is necessary to fight this pest by spraying the shrubs with "Aktellik" or "Karbofos", when the buds just bud.
A spider mite is located on the underside of the leaves and is woven over with a spider web. Over time, these leaves dry and fall off, as the tick sucks the juice out of them. To destroy the pest, you can spray raspberry acaricides. And with a large number of pests, plants need to be processed up to 4 times per season with an interval of 10 days.
Assortment Overview
Raspberries can be common, large-fruited, standard and remontant. Ordinary varieties unpretentious care and perfectly adapted to different climatic and weather conditions. The disadvantage is not very big fruits and not such a bountiful harvest as every summer resident would like.
In large-fruited raspberries sweet and juicy berries and increased yield. Standard raspberry in appearance resembles a tree and reaches 1.5 meters tall. The advantage of this variety is that you do not need special supports.
Those who want to feast on juicy berries as early as possible are choosing the repair raspberries, because this variety produces crops in the first year of planting, and then bears fruit twice a year - in summer and late autumn.
Universal raspberry varieties optimally meet the requirements of gardeners and are suitable for different types of climates. Consider the most popular types.
- "Aborigine" with a tall bush up to 2 meters without thorns. Harvest from one bush - 5-7 kg. Fruits turn out large, with fragrant pulp and sourish taste.The variety is resistant to diseases and is almost unaffected by pests. Winter hardiness is average, so it is suitable for growing in the south or in central Russia.
- "Alenushka" has more sour berries, so not everyone likes them raw, but such raspberries will be just right for making jam. The bush grows up to 2.2 meters in height, so the yield of this variety is quite high - up to 13 kg from a bush.
Variety distinguishes resistance to pests and high temperatures. Therefore, this type is suitable for the southern regions of the country.
- Variety "Faith" give gardeners medium-sized, but the sweetest fruit. Productivity reaches 5 kg from a bush, the variety is resistant to pests and drought, although frequent watering will only improve the taste and fruitfulness of raspberries.
- Canadian Raspberry has sweet berries and high yield (up to 12 kg). Its advantage - the berries can be stored for a long time. The plant can withstand summer heat and drought.
- Marlboro will bring up to 13 kg of raspberry from a bush of sweet and large fruits. The height of an erect shrub reaches 2.5 meters, so it is recommended to trim it from time to time in order to increase the yield.
- "Meteor" does not have a high yield (up to 2 kg from a bush), but it is one of the first to ripen - in June you will be able to feast on juicy berries. The advantage of this variety is resistance to fungal diseases and good frost resistance, so it can be grown in the north, the Urals and in Siberia.
- "Taganka" late ripening is also suitable for the northern regions, as the variety is able to withstand temperatures up to -20 degrees Celsius without being harbor. Productivity makes 4-5 kg from a bush. The variety is resistant to diseases and extreme weather conditions.
Early
Early ripe raspberries can not boast of high yields, but already in late May - early June, it will delight summer residents with the first juicy berries. Of the varieties popular in the opinion of gardeners, we note a few.
- "Scarlet Sails" has a yield of up to 1.7 kg. It is a winter-hardy variety - in the case of freezing of the main buds, the plant will still produce a crop using axillary buds.
- "The Runaway" gives up to 2 kg of fruit from the bush, and raspberry has an unusual apricot shade and delicate aroma. The grade differs in high frost resistance.
- "Patricia" - large-fruited variety with good yield (up to 5 kg). The berries do not fall apart and do not crumble, while juicy, ripe and sweet.
Winter hardiness of a grade is average, so use it in more southern regions or bend down and hide shoots for snow in the winter. The variety is disease resistant.
Mid season
Most summer residents choose mid-season varieties, as they give fruit relatively early, without losing their yield, as early varieties. This group does not require such care as early raspberry and is more resistant to diseases. Consider the most productive and popular varieties.
- "Tarusa" or popularly "raspberry tree". Its height reaches 1.8 m, and the yield is 6 kg. What distinguishes a variety from others is that there are no thorns on the branches, which means that the harvest process is simplified to the maximum. This variety matures in the second decade of July.
- "Hussar" has a yield of up to 3 kg per bush. Ruby berries have a pleasant sweet-sour taste. Winter hardiness at a grade is average, but he is not afraid of droughts and is steady against diseases.
- "Zeus" valued by summer residents for a special shape and appearance. Its oblong berries are located on the side branches in groups of 12-14 pieces. With abundant watering and proper care, such a bush can harvest up to 12 kg.
- "Glen Ampl" was bred in England, and the fruits can grow on the shoots of the previous year. The berries are medium in size and tasty. The advantages of the variety are winter hardiness, drought resistance and resistance to diseases and pests.
Late
Late ripening varieties have one drawback - you have to wait for the berries to the edge of summer or early autumn. But there are plenty of advantages: they are not afraid of frosts, they give high yields, they are distinguished by high winter resistance.
- "Kirzhach" gives a harvest up to 6 kg from a bush. The variety is resistant to low temperatures, dry weather and undemanding of soil fertility.
- "Patricia is late". The variety is similar to “Kirzhach”, but it has a long ripening period.
- "Mirage" - high-yielding variety with large elongated berries. Even when fully ripe berries are not showered. Winter-hardy and resistant to diseases and pests.
Remontnaya
Remontant varieties will allow to collect a very large amount of the crop.
- "Penguin" It has a standard crown type and consists of a small number of shoots. Harvest arrives in early September. Berries of dark crimson color are rounded, resistant to diseases and pests. The yield from the bush is quite high - up to 15 kg.
- "Indian summer". The harvest ripens in the second half of August, and the harvest continues until the frosts themselves. The berries are small, taste sweet and sour and aromatic. The variety is popular because of the abundant fruiting and excellent quality berries.
- "Hercules" has large fruits and straight-growing shoots that do not require support. Crop ripens in early August, and fruiting lasts until the first frost. The popularity of this variety is due to stable yields, resistance to fungal diseases and raspberry mite.
Gardeners tips
Here is what you need to know:
- Raspberry grows better in full sun, but if there is not enough space on the site, it will withstand a little shade. She loves a more acidic soil (pH 6.0-6.5). But in alkaline soil will suffer from excess iron and manganese deficiency.
- If you grow raspberries in a greenhouse, experienced gardeners recommend that in warm weather (at least 20 degrees Celsius), remove end frames from the frame in order to provide raspberries with not only fresh air, but also useful insects.
- To raspberry berries were large, learn how to water the plant. Irrigate not the aboveground part, but the basal one, so that the moisture does not evaporate from the leaves. If you notice that greens are beginning to fade - this is a sign that watering needs to be intensified. In addition, during a drought, the plant will be loosened by the soil under a bush so that oxygen is supplied to the roots.
- If you planted a lot of raspberry bushes, then there is a little trick that will help to harvest from different bushes with small time intervals and, accordingly, make sure that ripe berries do not crumble. When cutting in spring, make it different heights.
To do this, conditionally divide the bushes into 3 groups. The first one is cut by 10-15 cm, the second - by half the height, and in the third one, leave only 15-20 cm. In this case, the fruit will ripen consistently and not simultaneously. And you will have free time to remove all the berries, even from a large raspberries.
And in order not to be upset because of the lack of a rich harvest, do not grow raspberries in one place for more than four years, but transplant to a new place.
On how to grow raspberries, see the following video.