What to plant after potatoes next year?

When the new season begins, many gardeners have a question in their head: what can be planted on the beds where the potatoes grew earlier.On the one hand, the vast space has lost its nutrients, and not every plant will be able to successfully develop on such a soil. In addition, disease spores remained in the soil, and pests have already chosen the place. On the other hand, to arrange long-term idle time in such vast areas as potatoes usually take is also not an option. In order not to incur losses, it is necessary to make the right choice.
Special features
To begin with, it should be mentioned that after the potato season, the soil is very depleted - this crop is in the leading positions in the absorption of useful elements. Some growers decide that after a busy season the land rests. However, the surface itself can only recover in a few years, up to four. But during this time, everything will grow weed, and the owner of the plot will deprive himself of a significant share of the possible harvest.
Other gardeners prefer siderats - they wait until they reach a height of 15 centimeters, and then dig up them, digging them into the soil. However, in any case, the question remains what to plant next.
It should be remembered that the potato deprives the humus of phosphorus and potassium - therefore, these elements will have to be “returned” on their own, making the appropriate fertilizers. Next to solve the issue with pests. Wireworm larvae, nematodes and, of course, the Colorado potato beetle remain in the soil after potatoes. If in the next season they plant potatoes again on these beds, then, of course, they will be exposed to the active influence of insects. It is impossible to plant other crops that attract such pests.
After potatoes, phytophtora spores will also remain in the ground, and they can persist there for up to five years. Again, the return of this culture to the beds will be provided with problems. Finally, the soil may already be overfilled with pathogenic microorganisms actively secreted by the root system of potatoes.
Returning to the former potato beds, the first thing they will have to restore is to get rid of the shortcomings, remove the pests and restore fertility. To solve this problem, a tool such as seeding is often used. As soon as the fruits of potatoes are extracted (usually this happens in late August or early September), mustard, oats, rye, peas and other crops with similar properties are immediately planted on these beds.
It is necessary to wait until the height of the stems reaches at least 10 or 15 centimeters, and then dig up the soil, as if "interfering" in it the appeared plants. Thus, the soil is enriched with nitrogen and will be spared from the wireworm.
In addition, siderates increase air permeability, improve soil structure, normalize the balance of acids and alkalis, and stop the leaching of useful elements. There is also an option to leave the green mass for the winter, and dig up the beds in the spring. In this case, the land can recover better, but it is important not to allow the moment when harm comes instead of good, and planted crops become common weeds.
It is very easy to sow the green manure - you need to scatter the seeds in the beds, and then mulch it with the help of humus or compost. At the end of the procedure, the land is irrigated abundantly, and before the arrival of the cold, it is dug up. When the greening is carried out in the spring, the seeds will need to be deepened in rows by 3 or 4 centimeters into the soil, and then watered.
After preparing the soil, the crop rotation table becomes the main one - it is by it that the ideal followers are determined. Its essence is that there is a selection of crops depending on the requirements of specific nutrients. Some cultures impoverish the soil, others enrich, and it is important to learn how to build them in the correct sequence. Using this tool, you can achieve a good soil and a bountiful harvest on an ongoing basis.
Crop rotation is based on the conditional classification of all planted plants depending on the need for nutrients.
- Representatives of the first group for the development of quality requires nitrogen - this is usually leafy crops: lettuce, cabbage, spinach, and others.
- The second group consists of crops in need of phosphorus. These include fruit: squash, pumpkin, cucumber and zucchini.
- Plants from the third group feel bad if there is a shortage of potassium in the soil. These are root vegetables such as onions, carrots and potatoes.
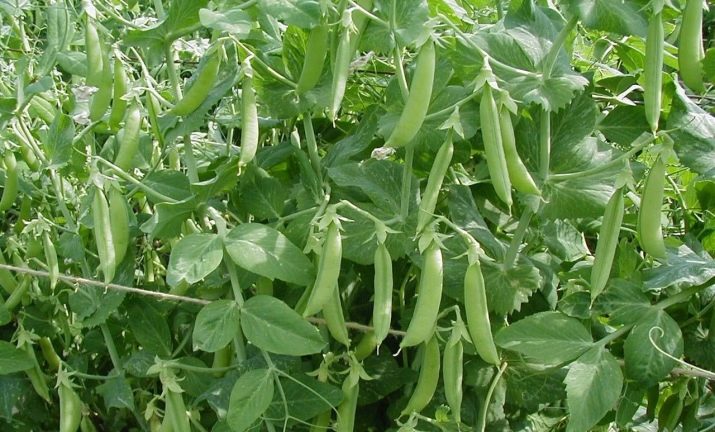
- Finally, the cultures of the fourth group do not need anything, but they themselves saturate the earth with nitrogen. In addition, their roots loosen and drain the soil. Of course, they are considered the best predecessors for most followers. Such "miracle plants" include peas, beans, lentils and beans.
In a nutshell, the principle of crop rotation is to plant those crops that require other elements, as well as to avoid those who are prone to similar diseases. If everything is right, then the soil will have time to rest from its predecessor, and the follower’s harvest will be good.
What can be planted?
Plant after potatoes next year can be very different vegetables. In addition to the siderats, right after the solanaceae, the planting of legumes and some cruciferous species will be excellent.
The roots will have enough nutrient residue in the soil, so the harvest can be collected even in the fall. Beans, peas and beans are considered the best followers.
Due to the fact that the nitrogenous tubers will appear on their root system, the soil will be enriched. In addition, green elements will fill it with potassium and phosphorus.
Gardeners who are also herders are better off planting crops that animals can eat. These include plants such as clover, alfalfa and the like.
If these crops turn out to be also honey plants, then the benefits will double, because the attracted pollinators will increase the yield. Oat and rye are planted from cereal sideratov. In addition to the nutrient content of the sprouts, other parts of the plant also benefit. For example, the rye root system is capable of producing a substance that has a detrimental effect on the fungus. As for cruciferous, experts recommend mustard, turnip, rutabaga and radish.
In the spring after siding on the garden you can send cucumbers and pumpkin. Without pretreatment of the soil, it will not work, as these crops will not have enough nutrients and they will get sick. In addition, a good harvest will give garlic (both winter and spring), celery, and parsnips. Successful results can be expected by planting beets and corn. You should also pay attention to carrots and onions.
In the spring it is also allowed to plant cabbage and legumes. However, the first may be problems. For the development of cabbage, especially white cabbage, requires a lot of nutrients, and the same as the potato.
The impoverished soil, even considering feeding, does not always cope with the situation. Therefore, cabbage can be planted, but only when the garden area is limited, and there are simply no other possibilities. The same applies to dill with parsley: planting is not worth it, but if there are no other possibilities, then allowed. In addition, it is important to protect the vegetable from diseases. Strawberries and strawberries can be grown only after waiting a period of three years. They are often subjected to attacks of the wireworm and the bearfish, so they should be planted only when they manage to completely get rid of the larvae of these pests.
What is not recommended?
First of all, it is strictly forbidden to solanaceous crops on the former potato garden bed - tomatoes, eggplants with peppers and Physalis should not be planted.The reason is that all the nightshade, to which the potato belongs, are subject to the same diseases, and they are attacked by the same insects. Of course, this situation will have an extremely negative impact on the quantity and quality of the crop.
The peppers will not get along with a potato bed and a related pepper, which cannot be said about zucchini - they, on the contrary, will give a rich harvest. Sunflowers are banned, as they are subject to similar diseases, the spores of which, as already mentioned, are contained in the soil. In addition, as mentioned above, a bad idea would be to immediately plant beds with strawberries and strawberries.
Tips
To restore the soil in the country is relatively easy if you follow some important rules.
New crops in the garden should always be planted after enriching the soil with potassium and phosphorus. The first feeding is usually carried out in the spring.
As early as the previous fall, after harvesting, it was necessary to complete the “potato season” correctly. All existing tubers are extracted from the ground: small, cut, and rotted. Then the tops are collected and burned, as it increases the likelihood of soil diseases. The soil is dug and processed by a rake, after which you can sow the green manure.
You can return potatoes to the same bed no earlier than the beginning of the third season. In addition, it cannot grow in the same place for more than three years in a row - and these years will have to fertilize the soil abundantly and process it well. Both mineral and organic fertilizers are important. As the latter, available compost or the aforementioned siderates is usually chosen. Loves potatoes and wood ash, rich in microelements and capable of disinfecting the site. For the latter purpose, by the way, potassium permanganate with boric acid is also used.
Speaking about this vegetable, it is worth mentioning that it is just as important to find the right "neighbors" for it. Gardeners recommend planting marigolds, nasturtium and calendula around the perimeter of the beds or in the aisle. Well contacted potatoes with beans. It protects it from bruchusa, and it enriches the impoverished soil with nitrogen.
It is strictly prohibited to place tomatoes, sunflowers and fruit trees nearby, whose neighborhood increases the risk of phytophthora.
Finally, once in the five-year period it is recommended to give the site a rest and hold it “under steam”. While the soil comes back to normal, the potatoes should be moved to another place or temporarily, in general, abandon this solanaceous culture.
About what to plant after potatoes next year, see below.